Determining the one, two, three, or four long and short loci of human complement C4 in a major histocompatibility complex haplotype encoding C4A or C4B proteins
- PMID: 12224044
- PMCID: PMC378538
- DOI: 10.1086/342778
Determining the one, two, three, or four long and short loci of human complement C4 in a major histocompatibility complex haplotype encoding C4A or C4B proteins
Abstract
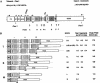
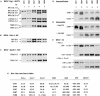
The complex genetics of human complement C4 with unusually frequent variations in the size and number of C4A and C4B, as well as their neighboring genes, in the major histocompatibility complex has been a hurdle for accurate epidemiological studies of diseases associated with C4. A comprehensive series of novel or improved techniques has been developed to determine the total gene number of C4 and the relative dosages of C4A and C4B in a diploid genome. These techniques include (1) definitive genomic restriction-fragment-length polymorphisms (RFLPs) based on the discrete duplication patterns of the RCCX (RP-C4-CYP21-TNX) modules and on the specific nucleotide changes for C4A and C4B isotypes; (2) module-specific PCR to give information on the total number of C4 genes by comparing the relative quantities of RP1- or TNXB-specific fragments with TNXA-RP2 fragments; (3) labeled-primer single-cycle DNA polymerization procedure of amplified C4d genomic DNA for diagnostic RFLP analysis of C4A and C4B; and (4) a highly reproducible long-range-mapping method that employs PmeI-digested genomic DNA for pulsed-field gel electrophoresis, to yield precise information on the number of long and short C4 genes in a haplotype. Applications of these vigorously tested techniques may clarify the roles that human C4A and C4B gene-dosage variations play in infectious and autoimmune diseases.
Figures
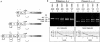

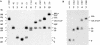
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Entrez Nucleotide, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?db=nucleotide (for C4A [accession number M59816-U07856-M58915], long C4B gene [accession number AF019413], short C4B gene [accession number AL049547 and U24578], RP1 or STK19 [accession numbers L26260 and L26261], RP2 [accession numbers L26262 and L26263], CYP21B [accession numbers M26856, M12792, M13936, and AF77974], CYP21A [accession numbers M26857, M12793, and M13935], TNXB [accession number U89337], and TNXA [accession numbers L26263 and U24488])
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for C4A [MIM 120810], C4B [MIM 120820], CYP21 and congenital adrenal hyperplasia [MIM 201910], RP1 or STK19 [MIM 604977], TNXB [MIM 600985], and SLE [MIM 152700])
References
-
- Atkinson JP, Schneider PM (1999) Genetic susceptibility and class III complement genes. In: Lahita RG (ed) Systemic lupus erythematosus. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 91–104
-
- Awdeh ZL, Raum D, Alper CA (1979) Genetic polymorphism of human complement C4 and detection of heterozygotes. Nature 282:205–208 - PubMed
-
- Baldwin WM III, Samaniego-Picota M, Kasper EK, Clark AM, Czader M, Rohde C, Zachary AA, Sanfilippo F, Hruban RH (1999) Complement deposition in early cardiac transplant biopsies is associated with ischemic injury and subsequent rejection episodes. Transplantation 68:894–900 - PubMed
-
- Bishof NA, Welch TR, Beischel LS (1990) C4B deficiency: a risk factor for bacteremia with encapsulated organisms. J Infect Dis 162:248–250 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

