Measurement of endotoxin activity in critically ill patients using whole blood neutrophil dependent chemiluminescence
- PMID: 12225611
- PMCID: PMC125316
- DOI: 10.1186/cc1522
Measurement of endotoxin activity in critically ill patients using whole blood neutrophil dependent chemiluminescence
Abstract
Background: Lipopolysaccharide (endotoxin) from the cell wall of Gram-negative bacteria is a potent trigger for the release of host-derived inflammatory mediators. The relationship between endotoxaemia, Gram-negative infection and the clinical syndrome of sepsis has been difficult to establish, in part because of the limitations of available endotoxin assays.
Methods: We performed an observational cohort study in critically ill patients in the medical/surgical intensive care unit (ICU) of a tertiary care hospital. Whole blood endotoxin levels on the day of ICU admission were measured using a novel chemiluminescent assay--the endotoxin activity assay (EAA)--and the chromogenic modification of the limulus amoebocyte lysate (LAL) assay.
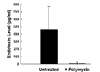
Results: We studied 74 consecutive admissions. Endotoxin levels were higher in patients with a diagnosis of sepsis (470 +/- 57 pg/ml) than in patients admitted with a diagnosis other than sepsis (157 +/- 140 pg/ml; P < 0.001). Endotoxaemia was significantly associated with Gram-negative infection (P < 0.05); no patient with a Gram-negative infection had an endotoxin level below 50 pg/ml. White blood cell counts of patients with EAA-detected endotoxaemia were significantly higher (15.7 +/- 9.1 x 10(9) cells/l for endotoxaemic patients versus 10.8 +/- 6.2 x 10(9) cells/l for patients without endotoxaemia; P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Endotoxaemia is associated with Gram-negative infection from any source, and with a diagnosis of sepsis and leukocytosis. These correlations were not apparent using the LAL method. The EAA may be a useful diagnostic tool for the investigation of invasive Gram-negative infection and incipient sepsis.
Figures

Comment in
-
Endotoxemia in critically ill patients: why a reliable test could be beneficial.Crit Care. 2002 Aug;6(4):289-90. doi: 10.1186/cc1511. Epub 2002 Jun 20. Crit Care. 2002. PMID: 12225599 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Endotoxaemia in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock.Intensive Care Med. 2000 May;26(5):538-44. doi: 10.1007/s001340051201. Intensive Care Med. 2000. PMID: 10923727
-
Endotoxaemia, fever and clinical status in immunosuppressed patients: a preliminary study.J Infect. 1987 Nov;15(3):201-6. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(87)92528-x. J Infect. 1987. PMID: 3693923
-
Combining intermediate levels of the Endotoxin Activity Assay (EAA) with other biomarkers in the assessment of patients with sepsis: results of an observational study.Crit Care. 2012 May 18;16(3):R88. doi: 10.1186/cc11350. Crit Care. 2012. PMID: 22607642 Free PMC article.
-
The detection and interpretation of endotoxaemia.Intensive Care Med. 2000;26 Suppl 1:S51-6. doi: 10.1007/s001340051119. Intensive Care Med. 2000. PMID: 10786959 Review.
-
Antibiotic induced endotoxin release and clinical sepsis: a review.J Chemother. 2001 Nov;13 Spec No 1(1):159-72. doi: 10.1179/joc.2001.13.Supplement-2.159. J Chemother. 2001. PMID: 11936361 Review.
Cited by
-
Labeled TEMPO-Oxidized Mannan Differentiates Binding Profiles within the Collectin Families.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 16;23(24):16067. doi: 10.3390/ijms232416067. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555720 Free PMC article.
-
The gut microbiota can be a potential regulator and treatment target of bone metastasis.Biochem Pharmacol. 2022 Mar;197:114916. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2022.114916. Epub 2022 Jan 15. Biochem Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35041811 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibiotic treatment modulates Escherichia coli-derived bacterial extracellular vesicle (BEV) production and their capacity to upregulate ICAM-1 in human endothelial cells.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 18:2025.05.12.653517. doi: 10.1101/2025.05.12.653517. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40463015 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Increased Endotoxin Activity in COVID-19 Patients Admitted to the Intensive Care Unit.J Intensive Care Med. 2023 Jan;38(1):27-31. doi: 10.1177/08850666221121734. Epub 2022 Sep 6. J Intensive Care Med. 2023. PMID: 36066033 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin 9 (PCSK9) function increases lipoteichoic acid clearance and improves outcomes in Gram positive septic shock patients.Sci Rep. 2019 Jul 22;9(1):10588. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-46745-0. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31332258 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parillo JE. Pathogenic mechanisms of septic shock. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:1471–1477. - PubMed
-
- Watson RWG, Redmond HP, Bouchier-Hayes D. Role of endotoxin in mononuclear phagocyte-mediated inflammatory responses. J Leukoc Biol. 1994;56:95–103. - PubMed
-
- Santos AA, Wilmore DW. The systemic inflammatory response: perspective of human endotoxemia. Shock. 1996;6(suppl 1):S50–S56. - PubMed
-
- Danner RL, Elin RJ, Hosseini JM, Wesley RA, Reilly JM, Parilllo JE. Endotoxemia in human septic shock. Chest. 1991;99:169–175. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

