Quality of life effects of antithrombin III in sepsis survivors: results from the KyberSept trial [ISRCTN22931023]
- PMID: 12225612
- PMCID: PMC125322
- DOI: 10.1186/cc1529
Quality of life effects of antithrombin III in sepsis survivors: results from the KyberSept trial [ISRCTN22931023]
Abstract
Introduction: Treatment of sepsis is aimed at increasing both the duration and quality of survival. A long-term focus on quality of life (QoL) in clinical trial evaluations of sepsis care should be a priority.
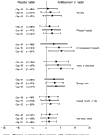
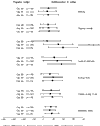
Method: QoL data were used to evaluate the effects of intravenous antithrombin III treatment for severe sepsis measured for up to 90 days during the follow-up phase of the KyberSept phase III clinical trial. A visual analog scale and a Karnofsky scale were used to measure physical, psychologic, and social QoL at regular intervals. Changes from baseline between placebo and antithrombin III groups were assessed using Wilcoxon statistical tests, with additional analyses by severity of illness and admitting diagnosis.
Results: Among all sepsis survivors in the trial, there was a significant advantage on some attributes of QoL in the antithrombin III subgroup of patients who did not receive heparin as compared with the corresponding placebo group.
Discussion: The present study represents the first attempt to evaluate patient QoL over a relatively long period in a large, randomized, placebo-controlled sepsis trial. Over a 90-day period, survivors of severe sepsis receiving antithrombin III experienced significant improvements as compared with placebo on several attributes of QoL. In conclusion, the present study demonstrated that clinical improvements over an extended time period with antithrombin III were complemented by improvements in QoL, particularly in social and psychologic functioning, in many patients.
Figures
Comment in
-
Looking beyond 28-day all-cause mortality.Crit Care. 2002 Aug;6(4):293-4. doi: 10.1186/cc1513. Epub 2002 Jul 8. Crit Care. 2002. PMID: 12225601 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cohen J, Guyatt G, Bernard GR, Thierry C, Cook D, Elbourne D, Marshall J, Nunn A, Opal S. New strategies for clinical trials in patients with sepsis and sepsis shock. Crit Care Med. 2001;29:880–886. - PubMed
-
- Perl TM, Dvorak L, Hwang T, Wenzel RP. Long-term survival and function after suspected gram-negative sepsis. JAMA. 1995;274:338–345. - PubMed
-
- Angus DC, Linde-Zwirble WT, Lidicker J, Clermont G, Carcillo J, Pinsky M. Epidemiology of severe sepsis in the United States: analysis of incidence, outcome, and associated costs of care. Crit Care Med. 2001;29:1303–1310. - PubMed
-
- Schaafsma J, Osoba D. The Karnofsky performance status scale re-examined: a cross-validation with the EORTC-C30. Qual Life Res. 1994;3:413–424. - PubMed
-
- O'Dell MW, Lubeck DP, O'Driscoll P, Matsuno S. Validity of the Karnofsky performance status in an HIV-infected sample. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1995;10:350–357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical