Mitochondrial-driven bicarbonate transport supports photosynthesis in a marine microalga
- PMID: 12226508
- PMCID: PMC166561
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.004598
Mitochondrial-driven bicarbonate transport supports photosynthesis in a marine microalga
Abstract
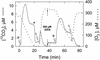
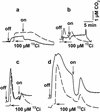
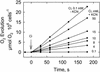
The CO(2)-concentrating mechanism (CCM) of the marine eustigmatophycean microalga Nannochloropsis gaditana consists of an active HCO(3)(-) transport system and an internal carbonic anhydrase to facilitate accumulation and conversion of HCO(3)(-) to CO(2) for photosynthetic fixation. Aqueous inlet mass spectrometry revealed that a portion of the CO(2) generated within the cells leaked to the medium, resulting in a significant rise in the extracellular CO(2) concentration to a level above its chemical equilibrium that was diagnostic for active HCO(3)(-) transport. The transient rise in extracellular CO(2) occurred in the light and the dark and was resolved from concurrent respiratory CO(2) efflux using H(13)CO(3)(-) stable isotope techniques. H(13)CO(3)(-) pump-(13)CO(2) leak activity of the CCM was unaffected by 10 microM 3(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea, an inhibitor of chloroplast linear electron transport, although photosynthetic O(2) evolution was reduced by 90%. However, low concentrations of cyanide, azide, and rotenone along with anoxia significantly reduced or abolished (13)CO(2) efflux in the dark and light. These results indicate that H(13)CO(3)(-) transport was supported by mitochondrial energy production in contrast to other algae and cyanobacteria in which it is supported by photosynthetic electron transport. This is the first report of a direct role for mitochondria in the energization and functioning of the CCM in a photosynthetic organism.
Figures



References
-
- Badger MR, Andrews TJ, Whitney SM, Ludwig M, Yellowlees DC, Leggat W, Price GD. The diversity and coevolution of Rubisco, plastids, pyrenoids, and chloroplast-based CO2-concentrating mechanisms in algae. Can J Bot. 1998;76:1052–1071.
-
- Badger MR, Spalding MH. CO2 acquisition, concentration and fixation in cyanobacteria and algae. In: Leegood RC, Sharkey TD, von Caemmerer S, editors. Photosynthesis: Physiology and Metabolism. Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers; 2000. pp. 369–397.
-
- Colman B, Huertas IE, Bhatti S, Dason JS. The diversity of inorganic carbon acquisition mechanisms in eukaryotic algae. Funct Plant Biol. 2002;29:261–270. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

