Genetic sophistication of human complement components C4A and C4B and RP-C4-CYP21-TNX (RCCX) modules in the major histocompatibility complex
- PMID: 12226794
- PMCID: PMC378539
- DOI: 10.1086/342777
Genetic sophistication of human complement components C4A and C4B and RP-C4-CYP21-TNX (RCCX) modules in the major histocompatibility complex
Abstract
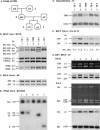
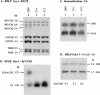
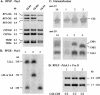
Human populations are endowed with a sophisticated genetic diversity of complement C4 and its flanking genes RP, CYP21, and TNX in the RCCX modules of the major histocompatibility complex class III region. We applied definitive techniques to elucidate (a) the complement C4 polymorphisms in gene sizes, gene numbers, and protein isotypes and (b) their gene orders. Several intriguing features are unraveled, including (1) a trimodular RCCX haplotype with three long C4 genes expressing C4A protein only, (2) two trimodular haplotypes with two long (L) and one short (S) C4 genes organized in LSL configurations, (3) a quadrimodular haplotype with four C4 genes organized in a SLSL configuration, and (4) another quadrimodular structure, with four long C4 genes (LLLL), that has the human leukocyte antigen haplotype that is identical to ancestral haplotype 7.2 in the Japanese population. Long-range PCR and PshAI-RFLP analyses conclusively revealed that the short genes from the LSL and SLSL haplotypes are C4A. In four informative families, an astonishingly complex pattern of genetic diversity for RCCX haplotypes with one, two, three and four C4 genes is demonstrated; each C4 gene may be long or short, encoding a C4A or C4B protein. Such diversity may be related to different intrinsic strengths among humans to defend against infections and susceptibilities to autoimmune diseases.
Figures




References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Entrez Nucleotide, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?db=nucleotide (for C4A [accession number M59816-U07856-M58915], long C4B gene [accession number AF019413], short C4B gene [accession numbers AL049547 and U24578], RP1 or STK19 [accession numbers L26260 and L26261], RP2 [accession numbers L26262 and L26263], CYP21B [accession numbers M26856, M12792, M13936, and AF77974], CYP21A [accession numbers M26857, M12793, and M13935], TNXB [accession number U89337], and TNXA [accession numbers L26263 and U24488])
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for C4A [MIM 120810], C4B [MIM 120820], CYP21 and CAH [MIM 201910], TNX [MIM 600985], RP1 or STK19 [MIM 604977], and SLE [MIM 152700])
References
-
- Awdeh ZL, Raum D, Alper CA (1979) Genetic polymorphism of human complement C4 and detection of heterozygotes. Nature 282:205–208 - PubMed
-
- Belt KT, Yu CY, Carroll MC, Porter RR (1985) Polymorphism of human complement component C4. Immunogenetics 21:173–180 - PubMed
-
- Blanchong CA, Chung EK, Rupert KL, Yang Y, Yang Z, Zhou B, Yu CY (2001) Genetic, structural and functional diversities of human complement components C4A and C4B and their mouse homologs, Slp and C4. Int Immunopharmacol 1:365–392 - PubMed
-
- Blanchong CA, Zhou B, Rupert KL, Chung EK, Jones KN, Sotos JF, Rennebohm RM, Yu CY (2000) Deficiencies of human complement component C4A and C4B and heterozygosity in length variants of RP-C4-CYP21-TNX (RCCX) modules in Caucasians: the load of RCCX genetic diversity on MHC-associated disease. J Exp Med 191:2183–2196 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

