Independent translocation of two micronemal proteins in developing Plasmodium falciparum merozoites
- PMID: 12228305
- PMCID: PMC128307
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.10.5751-5758.2002
Independent translocation of two micronemal proteins in developing Plasmodium falciparum merozoites
Abstract
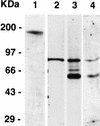
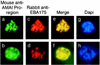
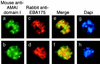
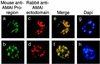
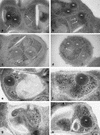
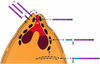
Apical membrane antigen 1 of Plasmodium falciparum (PfAMA1) contains an N-terminal propeptide that is removed prior to the translocation of the mature protein onto the merozoite surface. We localized unprocessed PfAMA1 to the microneme organelles of the intraerythrocytic schizont. The results have suggested that the processed form of PfAMA1 translocates from the microneme compartment independently of another microneme protein, EBA175, which is also involved in the invasion of human erythrocytes.
Figures

References
-
- Aikawa, M. 1966. The fine structures of the erythrocytic stages of three avian malarial parasites: Plasmodium fallax, P. lophurae and P. cathemerium. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 15:449-471. - PubMed
-
- Anders, R. F., P. E. Crewther, S. Edwards, M. Margetts, M. L. Matthew, B. Pollock, and D. Pye. 1998. Immunisation with recombinant AMA-1 protects mice against infection with Plasmodium chabaudi. Vaccine 16:240-247. - PubMed
-
- Anders, R. F., and A. Saul. 2000. Malaria vaccines. Parasitol. Today 16:444-447. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

