Characterization of a pore-forming cytotoxin expressed by Salmonella enterica serovars typhi and paratyphi A
- PMID: 12228306
- PMCID: PMC128311
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.10.5759-5769.2002
Characterization of a pore-forming cytotoxin expressed by Salmonella enterica serovars typhi and paratyphi A
Abstract
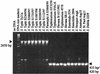
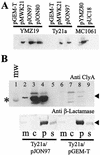
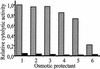
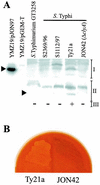
Cytolysin A (ClyA) is a pore-forming cytotoxic protein encoded by the clyA gene that has been characterized so far only in Escherichia coli. Using DNA sequence analysis and PCR, we established that clyA is conserved in the human-specific typhoid Salmonella enterica serovars Typhi and Paratyphi A and that the entire clyA gene locus is absent in many other S. enterica serovars, including Typhimurium. The gene products, designated ClyA(STy) and ClyA(SPa), show >/=90% amino acid identity to E. coli cytolysin A, ClyA(EC), and they are immunogenically related. The Salmonella proteins showed a pore-forming activity and are hence functional homologues to ClyA(EC). The chromosomal clyA(STy) gene locus was expressed at detectable levels in the serovar Typhi strains S2369/96 and S1112/97. Furthermore, in the serovar Typhi vaccine strain Ty21a, expression of clyA(STy) reached phenotypic levels, as detected on blood agar plates. The hemolytic phenotype was abolished by the introduction of an in-frame deletion in the clyA(STy) chromosomal locus of Ty21a. Transcomplementation of the mutant with a cloned clyA(STy) gene restored the hemolytic phenotype. To our knowledge, Ty21a is the first reported phenotypically hemolytic Salmonella strain in which the genetic determinant has been identified.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of iron on cytolysin A expression in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi.J Microbiol. 2009 Aug;47(4):479-85. doi: 10.1007/s12275-009-0039-4. Epub 2009 Sep 9. J Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19763423
-
ClyA cytolysin from Salmonella: distribution within the genus, regulation of expression by SlyA, and pore-forming characteristics.Int J Med Microbiol. 2009 Jan;299(1):21-35. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2008.06.004. Epub 2008 Aug 19. Int J Med Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 18715828
-
Molecular cloning and characterization of clyA genes in various serotypes of Salmonella enterica.J Microbiol. 2010 Oct;48(5):663-7. doi: 10.1007/s12275-010-9268-9. Epub 2010 Nov 3. J Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 21046345
-
Clinical pathogenesis of typhoid fever.J Infect Dev Ctries. 2008 Aug 30;2(4):260-6. doi: 10.3855/jidc.219. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2008. PMID: 19741286 Review.
-
The genome of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi.Clin Infect Dis. 2007 Jul 15;45 Suppl 1:S29-33. doi: 10.1086/518143. Clin Infect Dis. 2007. PMID: 17582565 Review.
Cited by
-
Detection of Typhoidal and Paratyphoidal Salmonella in Blood by Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction.Clin Infect Dis. 2015 Nov 1;61 Suppl 4(Suppl 4):S241-50. doi: 10.1093/cid/civ726. Clin Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 26449938 Free PMC article.
-
The Identification of Enteric Fever-Specific Antigens for Population-Based Serosurveillance.J Infect Dis. 2024 Mar 14;229(3):833-844. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiad242. J Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 37403670 Free PMC article.
-
Serologic evidence for effective production of cytolysin A in Salmonella enterica serovars typhi and paratyphi A during human infection.Infect Immun. 2006 Nov;74(11):6505-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00779-06. Epub 2006 Aug 21. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16923786 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of iron on cytolysin A expression in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi.J Microbiol. 2009 Aug;47(4):479-85. doi: 10.1007/s12275-009-0039-4. Epub 2009 Sep 9. J Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19763423
-
Seroepidemiology for Enteric Fever: Emerging Approaches and Opportunities.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2023 Jun 2;10(Suppl 1):S21-S25. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofad021. eCollection 2023 May. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37274530 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Atlung, T., and H. Ingmer. 1997. H-NS: a modulator of environmentally regulated gene expression. Mol. Microbiol. 24:7-17. - PubMed
-
- Braun, V., and T. Focareta. 1991. Pore-forming bacterial protein hemolysins (cytolysins). Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 18:115-158. - PubMed
-
- Buchmeier, N., S. Bossie, C. Y. Chen, F. C. Fang, D. G. Guiney, and S. J. Libby. 1997. SlyA, a transcriptional regulator of Salmonella typhimurium, is required for resistance to oxidative stress and is expressed in the intracellular environment of macrophages. Infect. Immun. 65:3725-3730. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Casadaban, M. J., and S. N. Cohen. 1980. Analysis of gene control signals by DNA fusion and cloning in Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 138:179-207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

