Interaction of adjacent primase domains within the hexameric gene 4 helicase-primase of bacteriophage T7
- PMID: 12228732
- PMCID: PMC130524
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.202471499
Interaction of adjacent primase domains within the hexameric gene 4 helicase-primase of bacteriophage T7
Abstract
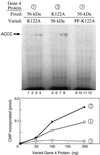
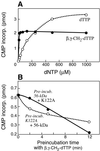
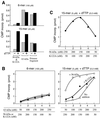
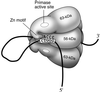
The interaction of primase monomers within the hexameric gene 4 helicase-primase of bacteriophage T7 has been examined by using two genetically distinct gene 4 proteins. The T7 56-kDa gene 4 protein differs from the full-length 63-kDa protein in that it lacks the N-terminal zinc motif essential for the recognition of primase recognition sites. A second gene 4 protein, gp4-K122A, is unable to catalyze the synthesis of phosphodiester bonds as the result of an amino acid change in the catalytic site. Although each protein alone is inactive, the two together catalyze the synthesis of RNA primers. Reconstitution of activity depends on hexamer formation. We propose that the zinc motif of one subunit in the hexamer interacts with the catalytic sites of adjacent subunits.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

