The suppression of brain cold-stable microtubules in mice induces synaptic defects associated with neuroleptic-sensitive behavioral disorders
- PMID: 12231625
- PMCID: PMC187434
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.223302
The suppression of brain cold-stable microtubules in mice induces synaptic defects associated with neuroleptic-sensitive behavioral disorders
Abstract
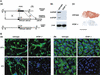
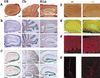
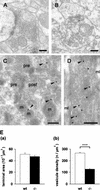
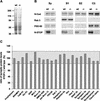
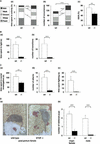
Neurons contain abundant subsets of highly stable microtubules that resist depolymerizing conditions such as exposure to the cold. Stable microtubules are thought to be essential for neuronal development, maintenance, and function. Previous work has indicated an important role of the microtubule-associated protein STOP in the induction of microtubule cold stability. Here, we developed STOP null mice. These mice were devoid of cold-stable microtubules. In contrast to our expectations, STOP-/- mice had no detectable defects in brain anatomy but showed synaptic defects, with depleted synaptic vesicle pools and impaired synaptic plasticity, associated with severe behavioral disorders. A survey of the effects of psychotropic drugs on STOP-/- mice behavior showed a remarkable and specific effect of long-term administration of neuroleptics in alleviating these disorders. This study demonstrates that STOP is a major factor responsible for the intriguing stability properties of neuronal microtubules and is important for synaptic plasticity. Additionally, STOP-/- mice may yield a pertinent model for study of neuroleptics in illnesses such as schizophrenia, currently thought to result from synaptic defects.
Figures

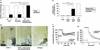
References
-
- Baas PW, Pienkowski TP, Cimbalnik KA, Toyama K, Bakalis S, Ahmad FJ, Kosik KS. Tau confers drug stability but not cold stability to microtubules in living cells. J Cell Sci. 1994;107:135–143. - PubMed
-
- Bear MF, Malenka RC. Synaptic plasticity: LTP and LTD. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1994;4:389–399. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
