Different metabotropic glutamate receptors play opposite roles in synaptic plasticity of the rat medial vestibular nuclei
- PMID: 12231639
- PMCID: PMC2290544
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.023424
Different metabotropic glutamate receptors play opposite roles in synaptic plasticity of the rat medial vestibular nuclei
Abstract
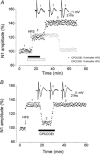
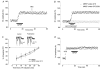
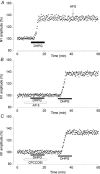
In the medial vestibular nuclei (MVN) of rat brainstem slices, the role of group II and III metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) and of the subtypes of group I mGluRs: mGluR1, mGluR5, was investigated in basal synaptic transmission and in the induction and maintenance of long-term potentiation (LTP). We used selective antagonists and agonists for mGluRs and we analysed the field potentials evoked by vestibular afferent stimulation before and after high-frequency stimulation (HFS) to induce LTP. The group II and III mGluR antagonist, (R,S)-alpha-2-methyl-4sulphonophenylglycine (MSPG), induced LTP per se and caused a reduction of the paired-pulse facilitation (PPF) ratio indicating an enhancement of glutamate release. This suggests that group II and III mGluRs are activated under basal conditions to limit glutamate release. Both the group II and III mGluR selective antagonists, 2S-2-amino-2-(1S,2S-2-carboxycycloprop-1-yl)-3-(xanth-9-yl)propanoate (LY341495) and (R,S)-alpha-methylserine-O-phosphate (MSOP), induced LTP, and the selective agonists, (2R,4R)-4-aminopyrrolidine-2,4-dicarboxylate (APDC) and L(+)-2-amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid (L-AP4) depressed the field potentials and prevented HFS-LTP, with a prevailing contribution of group II mGluRs over that of group III mGluRs. The mGluR1 antagonist, 7-(hydroxyimino)cyclopropa[b]chromen-1a-carboxylate ethyl ester (CPCCOEt) prevented the full development and maintenance of HFS-LTP. By contrast, the mGluR5 antagonist, 2-methyl-6-phenylethynylpyridine (MPEP) induced LTP per se, which was impeded by CPCCOEt, and it had no effect on LTP once induced by HFS. The PPF analysis showed an enhancement of glutamate release during MPEP potentiation. The group I mGluR agonist, (R,S)-3,5-dihydroxyphenylglycine (DHPG) induced LTP per se, which was blocked by CPCCOEt. By contrast the mGluR5 agonist, (R,S)-2-chloro-5-hydroxypheylglycine (CHPG) prevented LTP elicited by HFS and DHPG as well. In conclusion vestibular LTP is inhibited by group II and III mGluRs during the early induction phase while it is facilitated by mGluR1 for achieving its full expression and consolidation. An additional inhibitory control is exerted by mGluR5 at the level of this facilitatory phase.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Molecular mechanisms of group I metabotropic glutamate receptor mediated LTP and LTD in basolateral amygdala in vitro.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017 Feb;234(4):681-694. doi: 10.1007/s00213-016-4503-7. Epub 2016 Dec 28. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017. PMID: 28028604
-
Evidence for involvement of group II/III metabotropic glutamate receptors in NMDA receptor-independent long-term potentiation in area CA1 of rat hippocampus.J Neurophysiol. 1999 Dec;82(6):2956-69. doi: 10.1152/jn.1999.82.6.2956. J Neurophysiol. 1999. PMID: 10601432
-
Effects of metabotropic glutamate receptor block on the synaptic transmission and plasticity in the rat medial vestibular nuclei.Neuroscience. 1998 Nov;87(1):159-69. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(98)00138-9. Neuroscience. 1998. PMID: 9722149
-
(1R,2R)-N-(3-(4-[11C]Methoxyphenyl)-4-methylisothiazol-5-yl)-2-methylcyclopropane-carboxamide.2013 Jan 18 [updated 2013 Apr 11]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2013 Jan 18 [updated 2013 Apr 11]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 23586110 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
N-(4-(6-(Isopropylamino)pyrimidin-4-yl)-1,3-thiazol-2-yl)-N-methyl-4-[11C]methylbenzamide.2013 Feb 19 [updated 2013 May 2]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2013 Feb 19 [updated 2013 May 2]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 23638494 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Bidirectional plasticity gated by hyperpolarization controls the gain of postsynaptic firing responses at central vestibular nerve synapses.Neuron. 2010 Nov 18;68(4):763-75. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.09.025. Neuron. 2010. PMID: 21092864 Free PMC article.
-
Group II/III metabotropic glutamate receptors exert endogenous activity-dependent modulation of TRPV1 receptors on peripheral nociceptors.J Neurosci. 2011 Sep 7;31(36):12727-37. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6558-10.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21900552 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of visual experience on developmental shift from long-term depression to long-term potentiation in the rat medial vestibular nuclei.J Physiol. 2004 Nov 1;560(Pt 3):767-77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.069658. Epub 2004 Aug 26. J Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15331680 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of lead exposure on hippocampal metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 3 and 7 in developmental rats.J Negat Results Biomed. 2009 Apr 20;8:5. doi: 10.1186/1477-5751-8-5. J Negat Results Biomed. 2009. PMID: 19374778 Free PMC article.
-
A modulatory effect of the feedback from higher visual areas to V1 in the mouse.J Neurophysiol. 2013 May;109(10):2618-31. doi: 10.1152/jn.01083.2012. Epub 2013 Feb 27. J Neurophysiol. 2013. PMID: 23446698 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anwyl R. Metabotropic glutamate receptors: electrophysiological properties and role in plasticity. Brain Research Reviews. 1999;29:83–120. - PubMed
-
- Bortolotto ZA, Fitzjohn SM, Collingridge GL. Roles of metabotropic glutamate receptors in LTP and LTD in the hippocampus. Current Opinion in Neurobiology. 1999;9:299–304. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

