A possible dual site of action for carbon monoxide-mediated chemoexcitation in the rat carotid body
- PMID: 12231649
- PMCID: PMC2290549
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2001.015750
A possible dual site of action for carbon monoxide-mediated chemoexcitation in the rat carotid body
Abstract
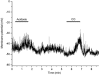
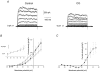
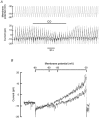
High tensions of carbon monoxide (CO), relative to oxygen, were used as a tool to investigate the mechanism of chemotransduction. In an in vitro whole organ, rat carotid body preparation, CO increased sinus nerve chemoafferent discharge in the dark, an effect that was significantly reduced (by ca 70 %) by bright white light and by the removal of extracellular Ca(2+) from the superfusate or by the addition of either Ni(2+) (2 mM) or methoxyverapamil (100 microM). Addition of the P(2) purinoceptor antagonist pyridoxalphosphate-6-azophenyl-2',4'-disulphonic acid (50 microM) also significantly reduced the neural response to CO. In perforated patch, whole-cell recordings of isolated rat type I cells, CO induced a depolarisation of ca 11 mV and a decrease in the amplitude of an outward current around and above the resting membrane potential. Membrane conductance between -50 and -60 mV was significantly reduced by ca 40 % by CO. These effects were not photolabile and were present also when a 'blocking solution' containing TEA, 4-AP, Ni(2+) and zero extracellular Ca(2+) was used. In conventional whole-cell recordings, CO only decreased current amplitudes above +10 mV and was without effect around the resting membrane potential. These data demonstrate a direct effect of CO upon type I cell K(+) conductances and strongly suggest an effect upon a background, leak conductance that requires an intracellular mediator. The photolabile effect of CO only upon afferent neural discharge adds further evidence to a dual site of action of CO with a separate action at the afferent nerve terminal that, additionally, requires the permissive action of the neurotransmitter ATP.
Figures




References
-
- Al-Hashem F, Barbe C, Kumar P. Interaction of ATP and CO2 upon carotid body chemosensitivity in vitro. Journal of Physiology. 2001;536.P:142P.
-
- Al-Hashem F, Conway AF, Kumar P. Calcium- and age-dependent effects of carbon monoxide upon chemodischarge in the rat carotid body in vitro. Journal of Physiology. 2000;523.P:296P.
-
- Anichkov SV, Belen'kii ML. Pharmacology of the Carotid Body Chemoreceptors. New York: Macmillan; 1963.
-
- Barbé C, Dubuis E, Vandier C, Kumar P. Effect of carbon monoxide on whole-cell currents of the isolated rat carotid body type I cell. Journal of Physiology. 2001;533.P:108–109P.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

