The imPaCT study: a randomised controlled trial to evaluate a hospital palliative care team
- PMID: 12232756
- PMCID: PMC2364271
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6600522
The imPaCT study: a randomised controlled trial to evaluate a hospital palliative care team
Abstract
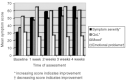
A randomised controlled trial was undertaken to assess the effectiveness of a hospital Palliative Care Team (PCT) on physical symptoms and health-related quality of life (HRQoL); patient, family carer and primary care professional reported satisfaction with care; and health service resource use. The full package of advice and support provided by a multidisciplinary specialist PCT ('full-PCT') was compared with limited telephone advice ('telephone-PCT', the control group) in the setting of a teaching hospital trust in the SW of England. The trial recruited 261 out of 684 new inpatient referrals; 175 were allocated to 'full-PCT', 86 to 'telephone-PCT' (2 : 1 randomisation); with 191 (73%) being assessed at 1 week. There were highly significant improvements in symptoms, HRQoL, mood and 'emotional bother' in 'full-PCT' at 1 week, maintained over the 4-week follow-up. A smaller effect was seen in 'telephone-PCT'; there were no significant differences between the groups. Satisfaction with care in both groups was high and there was no significant difference between them. These data reflect a high standard of care of patients dying of cancer and other chronic diseases in an acute hospital environment, but do not demonstrate a difference between the two models of service delivery of specialist palliative care.
Figures
References
-
- AaronsonNKAhmedzaiSBergmanBBullingerMCullADuezNJFilbertiAFlechtnerHFleishmanSBde HaesJCJMKaasaSKleeMOsobaDRazavidDRofeBSchraubSSneeuwKSullivanMTakedaF1993The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer QLQ-C30: A quality-of-life instrument for use in international trials in oncology J Natl Can Inst 85365375 - PubMed
-
- Addington-HallJMcCarthyM1995Dying from cancer: results of a national population-based investigation Pall Med 9295305 - PubMed
-
- Anonymous1989Terminal careless Br Med J 2991471
-
- ArandaS2000Changing paradigms in research: do we need to rethink the future? Progr Pall Care 8193197
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical