Genetic evidence that HNF-1alpha-dependent transcriptional control of HNF-4alpha is essential for human pancreatic beta cell function
- PMID: 12235114
- PMCID: PMC151122
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI15085
Genetic evidence that HNF-1alpha-dependent transcriptional control of HNF-4alpha is essential for human pancreatic beta cell function
Abstract
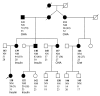
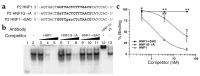
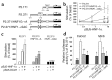
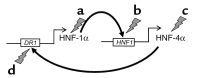
Mutations in the genes encoding hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha (HNF-4alpha) and HNF-1alpha impair insulin secretion and cause maturity onset diabetes of the young (MODY). HNF-4alpha is known to be an essential positive regulator of HNF-1alpha. More recent data demonstrates that HNF-4alpha expression is dependent on HNF-1alpha in mouse pancreatic islets and exocrine cells. This effect is mediated by binding of HNF-1alpha to a tissue-specific promoter (P2) located 45.6 kb upstream from the previously characterized Hnf4alpha promoter (P1). Here we report that the expression of HNF-4alpha in human islets and exocrine cells is primarily mediated by the P2 promoter. Furthermore, we describe a G --> A mutation in a conserved nucleotide position of the HNF-1alpha binding site of the P2 promoter, which cosegregates with MODY. The mutation results in decreased affinity for HNF-1alpha, and consequently in reduced HNF-1alpha-dependent activation. These findings provide genetic evidence that HNF-1alpha serves as an upstream regulator of HNF-4alpha and interacts directly with the P2 promoter in human pancreatic cells. Furthermore, they indicate that this regulation is essential to maintain normal pancreatic function.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A distant upstream promoter of the HNF-4alpha gene connects the transcription factors involved in maturity-onset diabetes of the young.Hum Mol Genet. 2001 Sep 15;10(19):2089-97. doi: 10.1093/hmg/10.19.2089. Hum Mol Genet. 2001. PMID: 11590126
-
Mutations in the hepatocyte nuclear factor-4alpha gene in maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY1).Nature. 1996 Dec 5;384(6608):458-60. doi: 10.1038/384458a0. Nature. 1996. PMID: 8945471
-
Functional study of the E276Q mutant hepatocyte nuclear factor-4alpha found in type 1 maturity-onset diabetes of the young: impaired synergy with chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor II on the hepatocyte nuclear factor-1 promoter.Diabetes. 1999 May;48(5):1162-7. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.48.5.1162. Diabetes. 1999. PMID: 10331424
-
A genetic switch in pancreatic beta-cells: implications for differentiation and haploinsufficiency.Diabetes. 2002 Aug;51(8):2355-62. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.51.8.2355. Diabetes. 2002. PMID: 12145145 Review.
-
Different genes, different diabetes: lessons from maturity-onset diabetes of the young.Ann Med. 2002;34(3):207-16. Ann Med. 2002. PMID: 12173691 Review.
Cited by
-
Pancreatic and duodenal homeobox gene 1 (Pdx1) down-regulates hepatic transcription factor 1 alpha (HNF1α) expression during reprogramming of human hepatic cells into insulin-producing cells.Am J Transl Res. 2015 Jun 15;7(6):995-1008. eCollection 2015. Am J Transl Res. 2015. PMID: 26279745 Free PMC article.
-
HNF1A Mutations and Beta Cell Dysfunction in Diabetes.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 16;23(6):3222. doi: 10.3390/ijms23063222. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35328643 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disruption of Tumor Suppressors HNF4α/HNF1α Causes Tumorigenesis in Liver.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Oct 26;13(21):5357. doi: 10.3390/cancers13215357. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34771521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pancreatic atrophy caused by dietary selenium deficiency induces hypoinsulinemic hyperglycemia via global down-regulation of selenoprotein encoding genes in broilers.PLoS One. 2017 Aug 1;12(8):e0182079. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0182079. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28763492 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of novel variants in PIK3C3, INSR and MAP3K4 of the ATM pathway genes with pancreatic cancer risk.Am J Cancer Res. 2020 Jul 1;10(7):2128-2144. eCollection 2020. Am J Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32775006 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yamagata K, et al. Mutations in the hepatocyte nuclear factor-4alpha gene in maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY1) Nature. 1996;384:458–460. - PubMed
-
- Froguel P, et al. Familial hyperglycemia due to mutations in glucokinase. Definition of a subtype of diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:697–702. - PubMed
-
- Yamagata K, et al. Mutations in the hepatocyte nuclear factor-1alpha gene in maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY3) Nature. 1996;384:455–458. - PubMed
-
- Stoffers DA, Ferrer J, Clarke WL, Habener JF. Early-onset type-II diabetes mellitus (MODY4) linked to IPF1. Nat Genet. 1997;17:138–139. - PubMed
-
- Horikawa Y, et al. Mutation in hepatocyte nuclear factor-1 beta gene (TCF2) associated with MODY. Nat Genet. 1997;17:384–385. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

