Metformin enhances insulin signalling in insulin-dependent and-independent pathways in insulin resistant muscle cells
- PMID: 12237252
- PMCID: PMC1573500
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704878
Metformin enhances insulin signalling in insulin-dependent and-independent pathways in insulin resistant muscle cells
Abstract
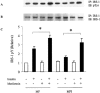
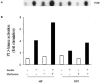
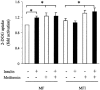
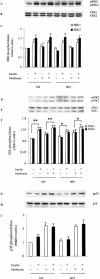
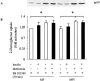
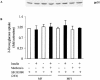
1 Metformin lowers blood glucose levels in type 2 diabetic patients. To evaluate the insulin sensitizing action of metformin on skeletal muscle cells, we have used C2C12 skeletal muscle cells differentiated in chronic presence or absence of insulin. 2 Metformin was added during the last 24 h of differentiation of the C2C12 myotubes. Insulin-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of insulin receptor (IR) and insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) was determined. 3 Chronic insulin treatment resulted in 60 and 40% reduction in insulin-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of IR and IRS-1, respectively. Treatment with metformin was able to increase the tyrosine phosphorylation of IR and IRS-1 by 100 and 90% respectively. 4 Chronic insulin treatment drastically reduced (45%) insulin-stimulated phosphatidyl inositol 3-kinase (PI 3-kinase) activity. Metformin treatment restored PI 3-kinase activity in insulin-resistant myotubes. 5 Insulin-stimulated glucose uptake was impaired in chronically insulin-treated myotubes. Metformin increased basal glucose uptake to significant levels (P<0.05), but metformin did not increase insulin-stimulated glucose transport. 6 All the three mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) were activated by insulin in sensitive myotubes. The activation of p38 MAPK was impaired in resistant myotubes, while ERK and JNK were unaffected. Treatment with metformin enhanced the basal activation levels of p38 in both sensitive and resistant myotubes, but insulin did not further stimulate p38 activation in metformin treated cells. 7 Treatment of cells with p38 inhibitor, SB203580, blocked insulin- and metformin-stimulated glucose uptake as well as p38 activation. 8 Since the effect of metformin on glucose uptake corresponded to p38 MAPK activation, this suggests the potential role p38 in glucose uptake. 9 These data demonstrate the direct insulin sensitizing action of metformin on skeletal muscle cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Gliclazide increases insulin receptor tyrosine phosphorylation but not p38 phosphorylation in insulin-resistant skeletal muscle cells.J Exp Biol. 2002 Dec;205(Pt 23):3739-46. doi: 10.1242/jeb.205.23.3739. J Exp Biol. 2002. PMID: 12409500
-
Tumor necrosis factor alpha produces insulin resistance in skeletal muscle by activation of inhibitor kappaB kinase in a p38 MAPK-dependent manner.J Biol Chem. 2004 Apr 23;279(17):17070-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M312021200. Epub 2004 Feb 4. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14764603
-
Arsenite stimulated glucose transport in 3T3-L1 adipocytes involves both Glut4 translocation and p38 MAPK activity.Eur J Biochem. 2003 Oct;270(19):3891-903. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1033.2003.03771.x. Eur J Biochem. 2003. PMID: 14511371
-
Insulin resistance and improvements in signal transduction.Endocrine. 2006 Feb;29(1):73-80. doi: 10.1385/ENDO:29:1:73. Endocrine. 2006. PMID: 16622294 Review.
-
Sending the signal: molecular mechanisms regulating glucose uptake.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2004 Jul;36(7):1212-7. doi: 10.1249/01.mss.0000132387.25853.3b. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2004. PMID: 15235328 Review.
Cited by
-
Antidiabetic and Hypolipidemic Activities of Curculigo latifolia Fruit:Root Extract in High Fat Fed Diet and Low Dose STZ Induced Diabetic Rats.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:601838. doi: 10.1155/2013/601838. Epub 2013 May 15. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013. PMID: 23762147 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin treatment in hyperglycemic critically ill patients: another challenge on the control of adverse outcomes.Iran J Pharm Res. 2011 Fall;10(4):913-9. Iran J Pharm Res. 2011. PMID: 24250430 Free PMC article.
-
Microalbuminuria in hyperglycemic critically ill patients treated with insulin or metformin.Iran J Pharm Res. 2011 Winter;10(1):141-8. Iran J Pharm Res. 2011. PMID: 24363693 Free PMC article.
-
Fructose Reduces Mitochondrial Metabolism and Increases Extracellular BCAA during Insulin Resistance in C2C12 Myotubes.Nutrients. 2024 May 23;16(11):1582. doi: 10.3390/nu16111582. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38892515 Free PMC article.
-
AKT ISOFORMS-AS160-GLUT4: The defining axis of insulin resistance.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2021 Dec;22(4):973-986. doi: 10.1007/s11154-021-09652-2. Epub 2021 Apr 30. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2021. PMID: 33928491 Review.
References
-
- AGUIRRE V., UCHIDA T., YENUSH L., DAVIS R., WHITE M.F. The c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase promotes insulin resistance during association with insulin receptor substrate-1 and phosphorylation of Ser307. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:9047–9054. - PubMed
-
- BORST S.E., SNELLEN H.G. Metformin, but not exercise training, increases insulin responsiveness in skeletal muscle of Sprague-Dawley rats. Life Sci. 2001;69:1497–1507. - PubMed
-
- CIARALDI T.P., KONG A.P.S., CHU N.V., KIM D.D., BAXI S., LOVISCACH M., PLODKOWSKI R., REITZ R., CAULFIELD M., MUDALIAR S., HENRT R.R. Regulation of glucose transport and insulin signaling by troglitazone or metformin in adipose tissue of type 2 diabetic subjects. Diabetes. 2002;51:30–36. - PubMed
-
- CONEJO R., VALVERDE A.V., BENITO M., LORENZO M. Insulin produces myogenesis in C2C12 myoblasts by induction of NF-κB and downregulation of AP-1 activities. J. Cell. Physiol. 2001;186:82–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

