Regulation of the avidity of ternary complexes containing the human 5-HT(1A) receptor by mutation of a receptor contact site on the interacting G protein alpha subunit
- PMID: 12237254
- PMCID: PMC1573502
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704880
Regulation of the avidity of ternary complexes containing the human 5-HT(1A) receptor by mutation of a receptor contact site on the interacting G protein alpha subunit
Abstract
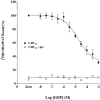
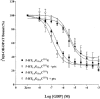
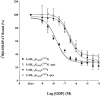
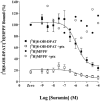
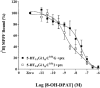
1 Fusion proteins were constructed between the human 5-HT(1A) receptor and pertussis toxin-resistant forms of both G(i1)alpha and G(o1)alpha mutated at residue(351) from cysteine to either glycine or isoleucine. Each of these was expressed stably in HEK293 cells. 2 Increasing concentrations of GDP inhibited binding of the agonist [(3)H]-8-OH-DPAT but not the antagonist [(3)H]-MPPF to each construct. 3 The IC(50) for GDP was greater for constructs containing isoleucine at residue(351) of the G proteins compared to those with glycine at this position. 4 The G protein antagonist suramin had similar effects to GDP on the binding of [(3)H]-8-OH-DPAT. 5 The proportion of 5-HT(1A) receptor binding sites detected by [(3)H]-MPPF that displayed high affinity for 8-OH-DPAT was significantly greater when the interacting G protein contained isoleucine rather than glycine at residue(351). 6 The 5-HT(1A) receptor displayed similar avidity of interaction with G(i1)alpha and G(o1)alpha. 7 These results indicate that a higher avidity ternary complex is formed between 8-OH-DPAT, the 5-HT(1A) receptor and G proteins when isoleucine rather than glycine is located at residue(351) of the interacting G protein.
Figures

Similar articles
-
S 14506: novel receptor coupling at 5-HT(1A) receptors.Neuropharmacology. 2001 Mar;40(3):334-44. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(00)00162-3. Neuropharmacology. 2001. PMID: 11166326
-
Mutation in a protein kinase C phosphorylation site of the 5-HT1A receptor preferentially attenuates Ca2+ responses to partial as opposed to higher-efficacy 5-HT1A agonists.Neuropharmacology. 2003 Jun;44(7):873-81. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(03)00097-2. Neuropharmacology. 2003. PMID: 12726819
-
Antagonist activity of meta-chlorophenylpiperazine and partial agonist activity of 8-OH-DPAT at the 5-HT(7) receptor.Eur J Pharmacol. 2000 May 12;396(1):1-8. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(00)00213-2. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10822046
-
Correlation between low/high affinity ratios for 5-HT(1A) receptors and intrinsic activity.Eur J Pharmacol. 1999 Dec 10;386(1):97-103. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(99)00738-4. Eur J Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10611469
-
Selective breeding of 5-HT(1A) receptor-mediated responses: application to emotion and receptor action.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2000 Dec;67(4):701-8. doi: 10.1016/s0091-3057(00)00415-9. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2000. PMID: 11166060 Review.
Cited by
-
The serotonin 5-HT7 receptors: two decades of research.Exp Brain Res. 2013 Oct;230(4):555-68. doi: 10.1007/s00221-013-3694-y. Epub 2013 Sep 17. Exp Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 24042216 Review.
References
-
- BAHIA D.S., WISE A., FANELLI F., LEE M., REES S., MILLIGAN G. Hydrophobicity of residue351 of the G-protein Gi1α determines the extent of activation by the α2A-adrenoceptor. Biochemistry. 1998;37:11555–11562. - PubMed
-
- BIRNBAUMER L., ABRAMOWITZ J., BROWN A.M. Receptor-effector coupling by G-proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1990;1031:163–224. - PubMed
-
- BURT A.R., SAUTEL M., WILSON M.A., REES S., WISE A., MILLIGAN G. Agonist-occupation of an α2A-adrenoceptor-Gi1α fusion protein results in activation of both receptor-linked and endogenous G proteins. Comparisons of their contributions to GTPase activity and signal transduction and analysis of receptor-G protein activation stoichiometry. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:10367–10375. - PubMed
-
- BUTKERAIT P., ZHENG Y., HALLAK H., GRAHAM T.E., MILLER H.A., BURRIS K.D., MOLINOFF P.B., MANNING D.R. Expression of the human 5-hydroxytryptamine1A receptor in Sf9 cells. Reconstitution of a coupled phenotype by co-expression of mammalian G protein subunits. J. Biol. Chem. 1995;270:18691–18699. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

