Interaction of different potassium channels in cardiac repolarization in dog ventricular preparations: role of repolarization reserve
- PMID: 12237256
- PMCID: PMC1573503
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704881
Interaction of different potassium channels in cardiac repolarization in dog ventricular preparations: role of repolarization reserve
Abstract
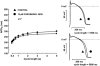
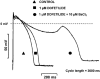
1 The aim of this study was to investigate the possible role of the interaction of different potassium channels in dog ventricular muscle, by applying the conventional microelectrode and whole cell patch-clamp techniques at 37 degrees C. 2 Complete block of I(Kr) by 1 micro M dofetilide lengthened action potential duration (APD) by 45.6+/-3.6% at 0.2 Hz (n=13). Chromanol 293B applied alone at 10 micro M (a concentration which selectively blocks I(Ks)) did not markedly lengthen APD (<7%), but when repolarization had already been prolonged by complete I(Kr) block with 1 micro M dofetilide, inhibition of I(Ks) with 10 micro M chromanol 293B substantially delayed repolarization by 38.5+/-8.2% at 0.2 Hz (n=6). 3 BaCl(2), at a concentration of 10 micro M which blocks I(Kl) without affecting other currents, lengthened APD by 33.0+/-3.1% (n=11), but when I(Kr) was blocked with 1 micro M dofetilide, 10 micro M BaCl(2) produced a more excessive rate dependent lengthening in APD, frequently (in three out of seven preparations) initiating early afterdepolarizations. 4 These findings indicate that if only one type of potassium channels is inhibited in dog ventricular muscle, excessive APD lengthening is not likely to occur. Dog ventricular myocytes seem to repolarize with a strong safety margin ('repolarization reserve'). However, when this normal 'repolarization reserve' is attenuated, otherwise minimal or moderate potassium current inhibition can result in excessive and potentially proarrhythmic prolongation of the ventricular APD. Therefore, application of drugs which are able to block more than one type of potassium channel is probably more hazardous than the use of a specific inhibitor of one given sort of potassium channel, and when simultaneous blockade of several kinds of potassium channel may be presumed, a detailed study is needed to define the determinants of 'repolarization reserve'.
Figures

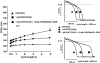



References
-
- ANTZELEVITCH C., SUN Z.Q., ZHANG Z.Q., YAN G.X. Cellular and ionic mechanisms underlying erythromycin-induced long QT intervals and torsade de pointes. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1996;28:1836–1848. - PubMed
-
- BOSCH R.F., GASPO R., BUSCH A.E., LANG H.J., NATTEL S. Effects of the chromanol 293B, a selective blocker of the slow component of the delayed rectifier K+ current, on repolarization in human and guinea pig ventricular myocytes. Cardiovasc. Res. 1998;38:441–450. - PubMed
-
- BRENDORP B., ELMING H., JUN L., KOBER L., MALIK M., JENSEN G.B., TORP-PEDERSEN C. The DIAMOND Study Group. QTc interval as a guide to select those patients with congestive heart failure and reduced left ventricular systolic function who will benefit from antiarrhythmic treatment with dofetilide. Circulation. 2001;103:1422–1427. - PubMed
-
- BURASHNIKOV A., ANTZELEVITCH C. Prominent IKs in epicardium and endocardium contributes to development of transmural dispersion of repolarization but protects against development of early afterdepolarizations. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2002;13:172–177. - PubMed
-
- BUSCH A.E., SUESSBRICH H., WALDEGGER S., SAILER E., GREGER R., LANG H., GIBSON K.J., MAYLIE J.G. Inhibition of IKs in guinea pig cardiac myocytes and guinea pig IsK channels by the chromanol 293B. Pflügers Archiv-Eur. J. Physiol. 1996;432:1094–1096. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

