Expression of functional neurotransmitter receptors in Xenopus oocytes after injection of human brain membranes
- PMID: 12237406
- PMCID: PMC130617
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.192445299
Expression of functional neurotransmitter receptors in Xenopus oocytes after injection of human brain membranes
Abstract
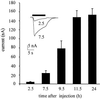
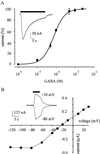
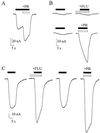
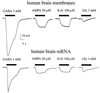
The Xenopus oocyte is a very powerful tool for studies of the structure and function of membrane proteins, e.g., messenger RNA extracted from the brain and injected into oocytes leads to the synthesis and membrane incorporation of many types of functional receptors and ion channels, and membrane vesicles from Torpedo electroplaques injected into oocytes fuse with the oocyte membrane and cause the appearance of functional Torpedo acetylcholine receptors and Cl(-) channels. This approach was developed further to transplant already assembled neurotransmitter receptors from human brain cells to the plasma membrane of Xenopus oocytes. Membranes isolated from the temporal neocortex of a patient, operated for intractable epilepsy, were injected into oocytes and, within a few hours, the oocyte membrane acquired functional neurotransmitter receptors to gamma-aminobutyric acid, alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid, kainate, and glycine. These receptors were also expressed in the plasma membrane of oocytes injected with mRNA extracted from the temporal neocortex of the same patient. All of this makes the Xenopus oocyte a more useful model than it already is for studies of the structure and function of many human membrane proteins and opens the way to novel pathophysiological investigations of some human brain disorders.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Microtransplantation of membranes from cultured cells to Xenopus oocytes: a method to study neurotransmitter receptors embedded in native lipids.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Mar 4;100(5):2896-900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0438006100. Epub 2003 Feb 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12595576 Free PMC article.
-
Microtransplantation of neurotransmitter receptors from cells to Xenopus oocyte membranes: new procedure for ion channel studies.Methods Mol Biol. 2006;322:347-55. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-000-3_24. Methods Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16739735 Review.
-
mRNAs coding for neurotransmitter receptors in rabbit and rat visual areas.J Neurosci Res. 1993 Aug 15;35(6):652-63. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490350608. J Neurosci Res. 1993. PMID: 8411267
-
Incorporation of acetylcholine receptors and Cl- channels in Xenopus oocytes injected with Torpedo electroplaque membranes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 May 23;92(11):5224-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.11.5224. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995. PMID: 7761478 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous transport systems in the Xenopus laevis oocyte plasma membrane.Methods. 2010 May;51(1):183-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2009.12.001. Epub 2009 Dec 4. Methods. 2010. PMID: 19963061 Review.
Cited by
-
Forebrain-selective AMPA-receptor antagonism guided by TARP γ-8 as an antiepileptic mechanism.Nat Med. 2016 Dec;22(12):1496-1501. doi: 10.1038/nm.4221. Epub 2016 Nov 7. Nat Med. 2016. PMID: 27820603
-
Expression of human epileptic temporal lobe neurotransmitter receptors in Xenopus oocytes: An innovative approach to study epilepsy.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Nov 12;99(23):15078-83. doi: 10.1073/pnas.232574499. Epub 2002 Oct 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12409614 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatase inhibitors remove the run-down of gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptors in the human epileptic brain.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Jul 6;101(27):10183-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0403683101. Epub 2004 Jun 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15218107 Free PMC article.
-
Working with OpusXpress: methods for high volume oocyte experiments.Methods. 2010 May;51(1):121-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2010.01.012. Epub 2010 Jan 18. Methods. 2010. PMID: 20085813 Free PMC article.
-
Xenopus Oocytes as a Powerful Cellular Model to Study Foreign Fully-Processed Membrane Proteins.Membranes (Basel). 2022 Oct 11;12(10):986. doi: 10.3390/membranes12100986. Membranes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36295745 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barnard E A, Miledi R, Sumikawa K. Proc R Soc London Ser B. 1982;215:241–246. - PubMed
-
- Gundersen C B, Miledi R, Parker I. Nature (London) 1984;308:421–424. - PubMed
-
- Miledi R, Parker I, Sumikawa K. Fidia Research Foundation Neuroscience Lectures. Vol. 3. New York: Raven; 1989. pp. 57–90.
-
- Sigel E. J Membr Biol. 1990;117:201–221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

