Cannabinoid receptor-G protein interactions: G(alphai1)-bound structures of IC3 and a mutant with altered G protein specificity
- PMID: 12237474
- PMCID: PMC2373710
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.0218402
Cannabinoid receptor-G protein interactions: G(alphai1)-bound structures of IC3 and a mutant with altered G protein specificity
Abstract
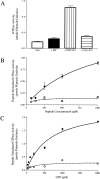
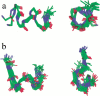
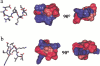
The structure of the C-terminal region of the third cytoplasmic loop (IC3) of the cannabinoid receptor one (CB1) bound to G(alphai1) has been determined using transferred nuclear Overhauser effects (NOEs). The wild-type IC3 sequence is helical when associated with G(alphai1). In contrast, a peptide containing the amino-acid inversion, Ala(341)-Leu(342) adopts a single turn. These findings correlate with the attenuated G(i) association of CB1 with the Ala(341)-Leu(342) mutation previously observed in vivo and the diminished stimulation of G(alphai1) GTPase activity by the corresponding peptide demonstrated in vitro here. These results, the first to report the structure of a GPCR domain while associated with G protein, imply the C-terminus of CB1 IC3, a region with high-sequence conservation among G-protein coupled receptors, must be helical for efficient coupling and activation of the G(i) protein.
Figures
References
-
- Abadji, V., Lucas-Lenard, J.M., Chin, C., and Kendall, D.A. 1999. Involvement of the carboxyl terminus of the third intracellular loop of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor in constitutive activation of Gs. J. Neurochem. 72 2032–2038. - PubMed
-
- Baker, D., Pryce, G., Croxford, J.L., Brown, P., Pertwee, R.G., Huffman, J.W., and Layward, L. 2000. Cannabinoids control spasticity and tremor in a multiple sclerosis model. Nature 404 84–87. - PubMed
-
- Boelens, R., Koning, T.M.G., van der Marel, G.A., Van Boom, H., and Kaptein, R. 1989. Iterative procedure for structure determination from proton-proton NOEs using a relaxation matrix approach, application to a DNA octamer. J. Magn. Reson. 82 290.
-
- Bonvin, A.M., Rullmann, J.A., Lamerichs, R.M., Boelens, R., and Kaptein, R. 1993. "Ensemble" iterative relaxation matrix approach: A new NMR refinement protocol applied to the solution structure of crambin. Proteins 15 385–400. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

