A phase I trial of antibody directed enzyme prodrug therapy (ADEPT) in patients with advanced colorectal carcinoma or other CEA producing tumours
- PMID: 12237768
- PMCID: PMC2364249
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6600517
A phase I trial of antibody directed enzyme prodrug therapy (ADEPT) in patients with advanced colorectal carcinoma or other CEA producing tumours
Abstract
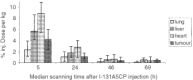
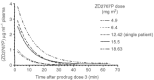
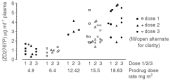
Antibody-directed enzyme prodrug therapy is a targeted therapy in which a prodrug is activated selectively at the tumour site by an enzyme, which has been targeted to the tumour by an antibody (antibody-enzyme conjugate). Previous clinical trials have shown evidence of tumour response, however, the activated drug had a long half-life, which resulted in dose-limiting myelosuppression. Also, the targeting system, although giving high tumour to blood ratios of antibody-enzyme conjugate (10 000 : 1) required administration of a clearing antibody in addition to the antibody-enzyme conjugate. The purpose of this current study therefore was to attempt tumour targeting of the antibody-enzyme conjugate without the clearing antibody, and to investigate a new prodrug (bis-iodo phenol mustard, ZD2767P) whose activated form is highly potent and has a short half-life. Twenty-seven patients were treated with antibody-directed enzyme prodrug therapy using A5CP antibody-enzyme conjugate and ZD2767P prodrug, in a dose-escalating phase I trial. The maximum tolerated dose of ZD2767P was reached at 15.5 mg m(-2)x three administrations with a serum carboxypeptidase G2 level of 0.05 U ml(-1). Myelosuppression limited dose escalation. Other toxicities were mild. Patients' quality of life was not adversely affected during the trial as assessed by the measures used. There were no clinical or radiological responses seen in the study, but three patients had stable disease at day 56. Human anti-mouse antibody and human anti-carboxypeptidase G2 antibody were produced in response to the antibody enzyme conjugate (A5CP). The antibody-enzyme conjugate localisation data (carboxypeptidase G2 enzyme levels by HPLC on tumour and normal tissue samples, and gamma camera analysis of I-131 radiolabelled conjugate) are consistent with inadequate tumour localisation (median tumour: normal tissue ratios of antibody-enzyme conjugate of less than 1). A clearance system is therefore desirable with this antibody-enzyme conjugate or a more efficient targeting system is required. ZD2767P was shown to clear rapidly from the circulation and activated drug was not measurable in the blood. ZD2767P has potential for use in future antibody-directed enzyme prodrug therapy systems.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Measurement of the critical DNA lesions produced by antibody-directed enzyme prodrug therapy (ADEPT) in vitro, in vivo and in clinical material.Br J Cancer. 2001 Jun 15;84(12):1671-6. doi: 10.1054/bjoc.2001.1843. Br J Cancer. 2001. PMID: 11401322 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody-directed enzyme prodrug therapy: efficacy and mechanism of action in colorectal carcinoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2000 Mar;6(3):765-72. Clin Cancer Res. 2000. PMID: 10741695 Clinical Trial.
-
Anti-tumour effects of an antibody-carboxypeptidase G2 conjugate in combination with phenol mustard prodrugs.Br J Cancer. 1995 Nov;72(5):1083-8. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1995.469. Br J Cancer. 1995. PMID: 7577451 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody-directed enzyme prodrug therapy (ADEPT) with mustard prodrugs.Anticancer Drug Des. 1995 Jul;10(5):361-72. Anticancer Drug Des. 1995. PMID: 7639927 Review.
-
Antibody directed enzyme prodrug therapy (ADEPT). A review of some theoretical, experimental and clinical aspects.Ann Oncol. 1994 Dec;5(10):879-91. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.annonc.a058725. Ann Oncol. 1994. PMID: 7696159 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Antibodies in Medicine.Molecules. 2023 Sep 5;28(18):6438. doi: 10.3390/molecules28186438. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37764213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel integrin-targeted binding-triggered drug delivery system for methotrexate.Pharm Res. 2011 Dec;28(12):3208-19. doi: 10.1007/s11095-011-0495-5. Epub 2011 Jun 22. Pharm Res. 2011. PMID: 21695561
-
Rapid Determination of Antibody-Antigen Affinity by Mass Photometry.J Vis Exp. 2021 Feb 8;(168):10.3791/61784. doi: 10.3791/61784. J Vis Exp. 2021. PMID: 33616097 Free PMC article.
-
Radiolabelling of glycosylated MFE-23::CPG2 fusion protein (MFECP1) with 99mTc for quantitation of tumour antibody-enzyme localisation in antibody-directed enzyme pro-drug therapy (ADEPT).Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2004 Aug;31(8):1090-6. doi: 10.1007/s00259-004-1474-4. Epub 2004 Mar 17. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2004. PMID: 15029458
-
Modifying an immunogenic epitope on a therapeutic protein: a step towards an improved system for antibody-directed enzyme prodrug therapy (ADEPT).Br J Cancer. 2004 Jun 14;90(12):2402-10. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601888. Br J Cancer. 2004. PMID: 15162148 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- AdamT1989Radioiodination for therapy Ann Clin Biochem 26244245 - PubMed
-
- BagshaweKDSharmaSK1996Cyclosporine delays host immune response to antibody enzyme conjugate in ADEPT Transplant Proc 2831563158 - PubMed
-
- BagshaweKSharmaSSpringerCAntoniwP1995Antibody directed enzyme prodrug therapy: a pilot scale clinical trial Tumour Targeting 11730
-
- BlakeyDCBurkePJDaviesDHDowellRIEastSJEckersleyKPFittonJEMcDaidJMeltonRGNiculescu-DuvazIAPinderPESharmaSKWrightAFSpringerCJ1996ZD2767, an improved system for antibody-directed enzyme prodrug therapy that results in tumour regressions in colorectal tumor xenografts Cancer Res 5632873292 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

