A secondary structure that contains the 5' and 3' splice sites suppresses splicing of duck hepatitis B virus pregenomic RNA
- PMID: 12239294
- PMCID: PMC136586
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.20.10195-10202.2002
A secondary structure that contains the 5' and 3' splice sites suppresses splicing of duck hepatitis B virus pregenomic RNA
Abstract
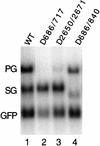
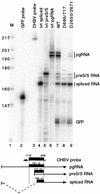
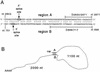
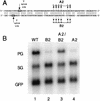
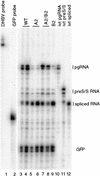
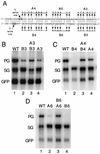
Pregenomic RNA (pgRNA) plays two major roles in the hepadnavirus life cycle. It is the mRNA for two proteins required for DNA replication, C and P, and it is the template for reverse transcription. pgRNA is a terminally redundant transcript whose synthesis does not involve RNA splicing. For duck hepatitis B virus (DHBV), a spliced RNA is derived from pgRNA by removal of a single intron. The mechanism for the simultaneous cytoplasmic accumulation of unspliced (pgRNA) and spliced RNA was not known. We found that mutations within two regions of the DHBV genome reduced the level of pgRNA while increasing the level of spliced RNA. One region is near the 5' end of pgRNA (region A), while the second is near the middle of pgRNA (region B). Inspection of the DHBV nucleotide sequence indicated that region A could base pair with region B. The 5' and 3' splice sites of the intron of the spliced RNA are within regions A and B, respectively. Substitutions that disrupted the predicted base pairing reduced the accumulation of pgRNA and increased the accumulation of spliced RNA. Restoration of base pairing, albeit mutant in sequence, resulted in restoration of pgRNA accumulation with a decrease in the level of spliced RNA. Our data are consistent with a model in which splicing of the pgRNA is suppressed by a secondary structure between regions A and B that occludes the splicing machinery from modifying pgRNA.
Figures

References
-
- Boris-Lawrie, K., T. M. Roberts, and S. Hull. 2001. Retroviral RNA elements integrate components of post-transcriptional gene expression. Life Sci. 69:2697-2709. - PubMed
-
- Buscher, M., W. Reiser, H. Will, and H. Schaller. 1985. Transcripts and the putative RNA pregenome of duck hepatitis B virus: implications for reverse transcription. Cell 40:717-724. - PubMed
-
- Chang, C., R. C. Hirsch, and D. Ganem. 1995. Sequences in the preC region of duck hepatitis B virus affect pregenomic RNA accumulation. Virology 207:549-554. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

