Promoter sequences required for reactivation of Epstein-Barr virus from latency
- PMID: 12239304
- PMCID: PMC136560
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.20.10282-10289.2002
Promoter sequences required for reactivation of Epstein-Barr virus from latency
Abstract
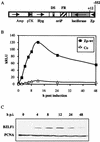
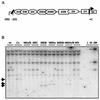
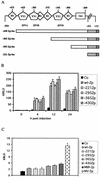
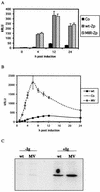
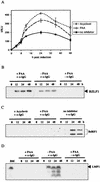
A luciferase reporter system with stably transfected oriP plasmids in Akata Burkitt's lymphoma cells provides a quantitative assay for the BZLF1 Zp promoter in response to B-cell receptor (BCR) activation by cross-linking with anti-immunoglobulin. In this system, detailed kinetic studies of promoter activity are possible. Previously reported promoter elements upstream of -221 from the transcription start and the ZIIR sequence had little effect on the Zp promoter, but the ZI and ZIIIA elements were essential for early activation. The ZIIIB element mediates autoactivation. Mutation of the ZV repressor sequence greatly increased the induction of the promoter but did not make it constitutively active. Zp transcription in response to BCR cross-linking declined after a few hours; this decline was reduced and delayed by acyclovir or phosphonoacetic acid, indicating that viral DNA replication or a late viral gene can play a role in the switch off of the Zp promoter. Late expression of the LMP1 protein may account for this.
Figures

References
-
- Bauer, G., P. Hofler, and M. Simon. 1982. Epstein-Barr virus induction by a serum factor. Characterization of the purified factor and the mechanism of its activation. J. Biol. Chem. 257:11411-11415. - PubMed
-
- Corcoran, E. E., and A. R. Means. 2001. Defining Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase cascades in transcriptional regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 276:2975-2978. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

