The NS2 proteins of parvovirus minute virus of mice are required for efficient nuclear egress of progeny virions in mouse cells
- PMID: 12239307
- PMCID: PMC136550
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.20.10307-10319.2002
The NS2 proteins of parvovirus minute virus of mice are required for efficient nuclear egress of progeny virions in mouse cells
Abstract
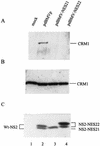
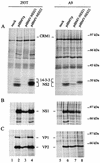
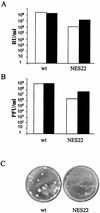
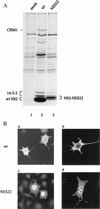
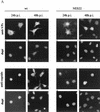
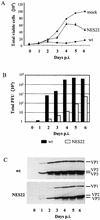
The small nonstructural NS2 proteins of parvovirus minute virus of mice (MVMp) were previously shown to interact with the nuclear export receptor Crm1. We report here the analysis of two MVM mutant genomic clones generating NS2 proteins that are unable to interact with Crm1 as a result of amino acid substitutions within their nuclear export signal (NES) sequences. Upon transfection of human and mouse cells, the MVM-NES21 and MVM-NES22 mutant genomic clones were proficient in synthesis of the four virus-encoded proteins. While the MVM-NES22 clone was further able to produce infectious mutant virions, no virus could be recovered from cells transfected with the MVM-NES21 clone. Whereas the defect of MVM-NES21 appeared to be complex, the phenotype of MVM-NES22 could be traced back to a novel distinct NS2 function. Infection of mouse cells with the MVM-NES22 mutant led to stronger nuclear retention not only of the NS2 proteins but also of infectious progeny MVM particles. This nuclear sequestration correlated with a severe delay in the release of mutant virions in the medium and with prolonged survival of the infected cell populations compared with wild-type virus-treated cultures. This defect could explain, at least in part, the small size of the plaques generated by the MVM-NES22 mutant when assayed on mouse indicator cells. Altogether, our data indicate that the interaction of MVMp NS2 proteins with the nuclear export receptor Crm1 plays a critical role at a late stage of the parvovirus life cycle involved in release of progeny viruses.
Figures

References
-
- Agbandje-McKenna, M., A. L. Llamas-Saiz, F. Wang, P. Tattersall, and M. G. Rossmann. 1998. Functional implications of the structure of the murine parvovirus minute virus of mice. Structure 6:1369-1381. - PubMed
-
- Askjaer, P., T. H. Jensen, J. Nilsson, L. Englmeier, and J. Kjems. 1998. The specificity of the CRM1-Rev nuclear export signal interaction is mediated by RanGTP. J. Biol. Chem. 273:33414-33422. - PubMed
-
- Avalosse, B., F. Dupont, and A. Burny. 1995. Gene therapy for cancer. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 7:94-100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

