A prenylation inhibitor prevents production of infectious hepatitis delta virus particles
- PMID: 12239323
- PMCID: PMC136538
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.20.10465-10472.2002
A prenylation inhibitor prevents production of infectious hepatitis delta virus particles
Abstract
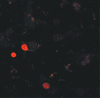
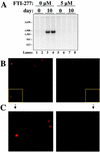
Hepatitis delta virus (HDV) causes both acute and chronic liver disease throughout the world. Effective medical therapy is lacking. Previous work has shown that the assembly of HDV virus-like particles (VLPs) could be abolished by BZA-5B, a compound with farnesyltransferase inhibitory activity. Here we show that FTI-277, another farnesyltransferase inhibitor, prevented the production of complete, infectious HDV virions of two different genotypes. Thus, in spite of the added complexity and assembly determinants of infectious HDV virions compared to VLPs, the former are also sensitive to pharmacological prenylation inhibition. Moreover, production of HDV genotype III virions, which is associated with particularly severe clinical disease, was as sensitive to prenylation inhibition as was that of HDV genotype I virions. Farnesyltransferase inhibitors thus represent an attractive potential class of novel antiviral agents for use against HDV, including the genotypes associated with most severe disease.
Figures
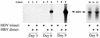
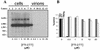

Similar articles
-
In vivo antiviral efficacy of prenylation inhibitors against hepatitis delta virus.J Clin Invest. 2003 Aug;112(3):407-14. doi: 10.1172/JCI17704. J Clin Invest. 2003. PMID: 12897208 Free PMC article.
-
Use of a prenylation inhibitor as a novel antiviral agent.J Virol. 1998 Nov;72(11):9303-6. doi: 10.1128/JVI.72.11.9303-9306.1998. J Virol. 1998. PMID: 9765479 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of the prenylation of K-Ras, but not H- or N-Ras, is highly resistant to CAAX peptidomimetics and requires both a farnesyltransferase and a geranylgeranyltransferase I inhibitor in human tumor cell lines.Oncogene. 1997 Sep;15(11):1283-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201296. Oncogene. 1997. PMID: 9315095
-
Prenylation of HDAg and antiviral drug development.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2006;307:133-49. doi: 10.1007/3-540-29802-9_7. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16903224 Review.
-
Management of hepatitis delta: Need for novel therapeutic options.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Aug 28;21(32):9461-5. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i32.9461. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26327754 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prenyltransferase Inhibitors: Treating Human Ailments from Cancer to Parasitic Infections.Medchemcomm. 2013 Mar;4(3):476-492. doi: 10.1039/C2MD20299A. Medchemcomm. 2013. PMID: 25530833 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of Novel Therapies for HDV.Viruses. 2022 Jan 28;14(2):268. doi: 10.3390/v14020268. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35215860 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vivo antiviral efficacy of prenylation inhibitors against hepatitis delta virus.J Clin Invest. 2003 Aug;112(3):407-14. doi: 10.1172/JCI17704. J Clin Invest. 2003. PMID: 12897208 Free PMC article.
-
Updates on Recent Advancements in Hepatitis D Virus Treatment.Viruses. 2025 Aug 10;17(8):1100. doi: 10.3390/v17081100. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40872814 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatitis D Virus: A Call to Screening.Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2014 Oct;10(10):647-86. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2014. PMID: 27540336 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Casey, J. L. 1998. Hepatitis delta virus: molecular biology, pathogenesis and immunology. Antivir. Therapy 3:37-42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

