Mechanism of e47-Pip interaction on DNA resulting in transcriptional synergy and activation of immunoglobulin germ line sterile transcripts
- PMID: 12242308
- PMCID: PMC139794
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.20.7337-7350.2002
Mechanism of e47-Pip interaction on DNA resulting in transcriptional synergy and activation of immunoglobulin germ line sterile transcripts
Abstract
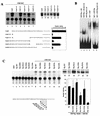
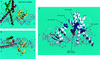
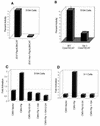
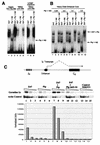
E47 and Pip are proteins crucial for proper B-cell development. E47 and Pip cooperatively bind to adjacent sites in the immunoglobulin kappa chain 3' enhancer and generate a potent transcriptional synergy. We generated protein-DNA computer models to visualize E47 and Pip bound to DNA. These models predict precise interactions between the two proteins. We tested predictions deduced from these models by mutagenesis studies and found evidence for novel direct interactions between the E47 helix-loop-helix domain (Arg 357 or Asp 358) and the Pip N terminus (Leu 24). We also found that precise spatial alignment of the binding sites was necessary for transcriptional synergy and cooperative DNA binding. A Pip dominant negative mutant that cannot synergize with E47 inhibited enhancer activity in plasmacytoma cells and could not activate transcription in pre-B cells. Using electrophoretic mobility shift assays, we found that Pip can bind to the heavy-chain intron enhancer region. In addition, we found that in fibroblasts Pip greatly increased E47 induction of germ line I micro transcripts associated with somatic rearrangement and isotype class switching. However, a Pip dominant negative mutant inhibited germ line I micro transcripts. The importance of these results for late B-cell functions is discussed.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Transcription factor Pip can enhance DNA binding by E47, leading to transcriptional synergy involving multiple protein domains.Mol Cell Biol. 1998 Aug;18(8):4639-50. doi: 10.1128/MCB.18.8.4639. Mol Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9671474 Free PMC article.
-
ETS-mediated cooperation between basic helix-loop-helix motifs of the immunoglobulin mu heavy-chain gene enhancer.Mol Cell Biol. 1998 Mar;18(3):1477-88. doi: 10.1128/MCB.18.3.1477. Mol Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9488464 Free PMC article.
-
Helix-loop-helix transcription factor E47 activates germ-line immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene transcription and rearrangement in a pre-T-cell line.Genes Dev. 1991 Aug;5(8):1367-76. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.8.1367. Genes Dev. 1991. PMID: 1714414
-
E47 activates the Ig-heavy chain and TdT loci in non-B cells.EMBO J. 1996 Sep 16;15(18):5014-21. EMBO J. 1996. PMID: 8890174 Free PMC article.
-
Overlapping expression of early B-cell factor and basic helix-loop-helix proteins as a mechanism to dictate B-lineage-specific activity of the lambda5 promoter.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 May;20(10):3640-54. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.10.3640-3654.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10779354 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
NFAT and IRF proteins regulate transcription of the anti-HIV gene, APOBEC3G.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jan 28;286(4):2567-77. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.154377. Epub 2010 Nov 15. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21078663 Free PMC article.
-
B-cell receptor activation inhibits AID expression through calmodulin inhibition of E-proteins.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Jan 29;105(4):1267-72. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0708220105. Epub 2008 Jan 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18203819 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon regulatory factor 4 and 8 in B-cell development.Trends Immunol. 2008 Oct;29(10):487-92. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2008.07.006. Epub 2008 Sep 3. Trends Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18775669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A developmentally controlled competitive STAT5-PU.1 DNA binding mechanism regulates activity of the Ig κ E3' enhancer.J Immunol. 2012 Mar 1;188(5):2276-84. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1102239. Epub 2012 Jan 25. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22279106 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic histone modifications do not control Igkappa locus contraction and intranuclear localization in cells with dual B cell-macrophage potential.J Immunol. 2006 Nov 1;177(9):6165-71. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.9.6165. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 17056545 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bain, G., E. C. R. Maandag, D. J. Izon, D. Amsen, A. M. Kruisbeek, B. C. Weintraub, I. Krop, M. S. Schlissel, A. J. Feeney, M. van Roon, M. van der Valk, H. P. J. te Riele, A. Berns, and C. Murre. 1994. E2A proteins are required for proper B cell development and initiation of immunoglobulin gene rearrangements. Cell 79:885-892. - PubMed
-
- Bain, G., and C. Murre. 1998. The role of E-proteins in B- and T-lymphocyte development. Semin. Immunol. 10:143-153. - PubMed
-
- Benezra, R., R. L. Davis, D. Lockshon, D. L. Turner, and H. Weintraub. 1990. The protein Id: a negative regulator of helix-loop-helix DNA binding proteins. Cell 61:49-59. - PubMed
-
- Betz, A. G., C. Milstein, A. Gonzalel-Fernandez, R. Pannell, T. Larson, and M. S. Neuberger. 1994. Elements regulating somatic hypermutation of an Igκ gene: critical role of the intron enhancer/matrix attachment region. Cell 77:239-248. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
