Functional correction of adult mdx mouse muscle using gutted adenoviral vectors expressing full-length dystrophin
- PMID: 12271128
- PMCID: PMC130572
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.202300099
Functional correction of adult mdx mouse muscle using gutted adenoviral vectors expressing full-length dystrophin
Abstract
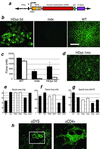
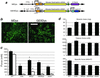
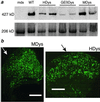
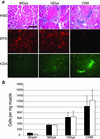
Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a lethal X-linked recessive disorder caused by mutations in the dystrophin gene. Delivery of functionally effective levels of dystrophin to immunocompetent, adult mdx (dystrophin-deficient) mice has been challenging because of the size of the gene, immune responses against viral vectors, and inefficient infection of mature muscle. Here we show that high titer stocks of three different gutted adenoviral vectors carrying full-length, muscle-specific, dystrophin expression cassettes are able to efficiently transduce muscles of 1-yr-old mdx mice. Single i.m. injections of viral vector restored dystrophin production to 25-30% of mouse limb muscle 1 mo after injection. Furthermore, functional tests of virally transduced muscles revealed almost 40% correction of their high susceptibility to contraction-induced injury. Our results show that functional abnormalities of dystrophic muscle can be corrected by delivery of full-length dystrophin to adult, immunocompetent mdx mice, raising the prospects for gene therapy of muscular dystrophies.
Figures
References
-
- Emery A E H. Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Oxford: Oxford Medical Publications; 1993.
-
- Miller R G, Hoffman E P. Neurol Clin. 1994;12:699–725. - PubMed
-
- Hoffman E P, Morgan J E, Watkins S C, Partridge T A. J Neurol Sci. 1990;99:9–25. - PubMed
-
- Sicinski P, Geng Y, Ryder-Cook A S, Barnard E A, Darlison M G, Barnard P J. Science. 1989;244:1578–1580. - PubMed
-
- Brooks S V. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1998;19:179–187. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

