The dual function of the splenic marginal zone: essential for initiation of anti-TI-2 responses but also vital in the general first-line defense against blood-borne antigens
- PMID: 12296846
- PMCID: PMC1906503
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2002.01953.x
The dual function of the splenic marginal zone: essential for initiation of anti-TI-2 responses but also vital in the general first-line defense against blood-borne antigens
Abstract
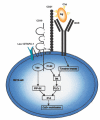
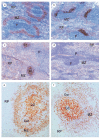
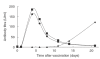
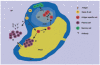
The splenic marginal zone (S-MZ) is especially well equipped for rapid humoral responses and is unique in its ability to initiate an immune response to encapsulated bacteria (T-cell independent type 2 (TI-2) antigens). Because of the rapid spreading through the blood, infections with blood-borne bacteria form a major health risk. To cope with blood-borne antigens, a system is needed that can respond rapidly to a great diversity of organisms. Because of a number of unique features, S-MZ B cells can respond rapid and efficient to all sorts of blood-borne antigens. These unique features include a low blood flow microenvironment, low threshold for activation, high expression of complement receptor 2 (CR2, CD21) and multireactivity. Because of the unique high expression of CD21 in a low flow compartment, S-MZ B cells can bind and respond to TI-2 antigens even with relatively low-avid B cell receptors. Although TI-2 antigens are in general poorly opsonized by classic opsonins, a particular characteristic of these antigens is their ability to bind very rapidly to complement fragment C3d without the necessity of previous immunoglobulin binding. TI-2 primed S-MZ B cells, already by first passage through the germinal centre, will meet antigen-C3d complexes bound to follicular dendritic cells, allowing unique immediate isotype switching. This explains that the primary humoral response to TI-2 antigens is unique in its characterization by a rapid increase in IgM concurrent with IgG antibody levels.
Figures
References
-
- Martin F, Oliver AM, Kearney JF. Marginal zone and B1 B cells unite in the early response against T-independent blood-borne particulate antigens. Immunity. 2001;14:617–29. - PubMed
-
- Timens W, Boes A, Poppema S. Human marginal zone B cells are not an activated B cell subset. strong expression of CD21 as a putative mediator for rapid B cell activation. Eur J Immunol. 1989;19:2163–6. - PubMed
-
- Guinamard R, Okigaki M, Schlessinger J, Ravetch JV. Absence of marginal zone B cells in Pyk-2-deficient mice defines their role in the humoral response. Nat Immunol. 2000;1:31–6. - PubMed
-
- Kraal G. Cells in the marginal zone of the spleen. Int Rev Cytol. 1992;132:31–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

