Changes in thymus volume in adult HIV-infected patients under HAART: correlation with the T-cell repopulation
- PMID: 12296862
- PMCID: PMC1906507
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2002.01950.x
Changes in thymus volume in adult HIV-infected patients under HAART: correlation with the T-cell repopulation
Abstract
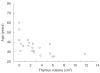
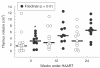
An important thymus role has been suggested in T-cell repopulation after HAART in adult HIV-1 infected patients. Thymus volume increase after treatment has been described in HIV-1 infected children but not in adult patients. The objective of this work was to evaluate the effect of HAART on the thymic volume of adult HIV-1 infected patients and its relation with the T-cell repopulation. Twenty-one adult patients following 24 weeks under HAART were included in the study. All patients underwent a thoracic computed tomography (CT) evaluation for the measurement of thymic volumes at weeks 0, 12 and 24. Baseline thymus volume showed a significant correlation with the patient's age. Thymic volume significantly increased after 24 weeks of HAART. Besides, a significant correlation between changes in the thymus volume and changes in both total and naïve CD4+ cell counts was found. Only patients with increases > or =100 CD4+ cell counts after treatment significantly increased the thymic volume. These data show the first evidence of an early change in thymic volume of adult HIV-1 infected patients under HAART. This increase was related to the rise of both total and naïve CD4+ cell counts suggesting a functional role of thymic volume increase.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparison of thymic function-related markers to predict early CD4 T-cell repopulation in adult HIV-infected patients on HAART.Antivir Ther. 2003 Aug;8(4):289-94. Antivir Ther. 2003. PMID: 14518697
-
Thymic volume is associated independently with the magnitude of short- and long-term repopulation of CD4+ T cells in HIV-infected adults after highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART).Clin Exp Immunol. 2004 Jun;136(3):501-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2004.02474.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15147352 Free PMC article.
-
Thymic function in HIV-infection.Dan Med J. 2013 Apr;60(4):B4622. Dan Med J. 2013. PMID: 23651726 Review.
-
Baseline thymic volume is a predictor for CD4 T cell repopulation in adult HIV-infected patients under highly active antiretroviral therapy.Antivir Ther. 2002 Sep;7(3):159-63. Antivir Ther. 2002. PMID: 12487382
-
Failure to reconstitute CD4+ T-cells despite suppression of HIV replication under HAART.AIDS Rev. 2006 Apr-Jun;8(2):88-97. AIDS Rev. 2006. PMID: 16848276 Review.
Cited by
-
Endogenous thymic regeneration: restoring T cell production following injury.Nat Rev Immunol. 2025 Jun;25(6):407-424. doi: 10.1038/s41577-024-01119-0. Epub 2025 Jan 6. Nat Rev Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39762553 Review.
-
Alcohol Types and HIV Disease Progression Among HIV-Infected Drinkers Not Yet on Antiretroviral Therapy in Russia and Uganda.AIDS Behav. 2017 Nov;21(Suppl 2):204-215. doi: 10.1007/s10461-017-1895-2. AIDS Behav. 2017. PMID: 28856539 Free PMC article.
-
Thymic hyperplasia after chemotherapy in adults with mature B cell lymphoma and its influence on thymic output and CD4(+) T cells repopulation.Oncoimmunology. 2016 Feb 18;5(5):e1137417. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2015.1137417. eCollection 2016 May. Oncoimmunology. 2016. PMID: 27467956 Free PMC article.
-
Different profiles of immune reconstitution in children and adults with HIV-infection after highly active antiretroviral therapy.BMC Infect Dis. 2006 Jul 13;6:112. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-6-112. BMC Infect Dis. 2006. PMID: 16839416 Free PMC article.
-
Poor immune reconstitution in HIV-infected patients associates with high percentage of regulatory CD4+ T cells.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57336. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057336. Epub 2013 Feb 20. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23437372 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Walker RE, Carter C, Muul L, et al. Peripheral expansion of pre-existing mature T cells is an important means of CD4+ T-cell regeneration HIV-infected adults. Nature Med. 1998;4:852–6. - PubMed
-
- Hazenberg MD, Clark DR, Miedema F. Tilted balance of T cell renewal in HIV-1 infection. AIDS Rev. 1999;1:67–73.
-
- McCune. Thymic function in HIV-1 disease. Immunology. 1997;9:397–404. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

