Inducible nitric oxide synthase is expressed in synovial fluid granulocytes
- PMID: 12296866
- PMCID: PMC1906489
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2002.01959.x
Inducible nitric oxide synthase is expressed in synovial fluid granulocytes
Abstract
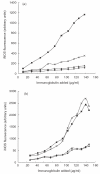
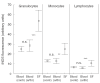
The objective of the study was to evaluate the NO-producing potential of synovial fluid (SF) cells. SF from 15 patients with arthritis was compared with blood from the same individuals and with blood from 10 healthy controls. Cellular expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) was analysed by flow cytometry. High-performance liquid chromatography was used to measure l-arginine and l-citrulline. Nitrite and nitrate were measured colourimetrically utilizing the Griess' reaction. Compared to whole blood granulocytes in patients with chronic arthritis, a prominent iNOS expression was observed in SF granulocytes (P < 0.001). A slight, but statistically significant, increase in iNOS expression was also recorded in lymphocytes and monocytes from SF. l-arginine was elevated in SF compared to serum (257 +/- 78 versus 176 +/- 65 micro mol/l, P = 0.008), whereas a slight increase in l-citrulline (33 +/- 11 versus 26 +/- 9 micro mol/l), did not reach statistical significance. Great variations but no significant differences were observed comparing serum and SF levels of nitrite and nitrate, respectively, although the sum of nitrite and nitrate tended to be elevated in SF (19.2 +/- 20.7 versus 8.6 +/- 6.5 micro mol/l, P = 0.054). Synovial fluid leucocytes, in particular granulocytes, express iNOS and may thus contribute to intra-articular NO production in arthritis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nitric oxide synthase is expressed in the lymphomononuclear cells of synovial fluid in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.J Rheumatol. 1999 Oct;26(10):2083-8. J Rheumatol. 1999. PMID: 10529121
-
Characterization of the induction of nitric oxide synthase and cyclo-oxygenase in rat aorta in organ culture.Br J Pharmacol. 1997 May;121(1):125-33. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701100. Br J Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9146896 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of nitric oxide synthases and effects of L-arginine and L-NMMA on nitric oxide production and fluid transport in collagenous colitis.Gut. 2001 Sep;49(3):387-94. doi: 10.1136/gut.49.3.387. Gut. 2001. PMID: 11511561 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of nitrite and nitrate in biological fluids by assays based on the Griess reaction: appraisal of the Griess reaction in the L-arginine/nitric oxide area of research.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2007 May 15;851(1-2):51-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2006.07.054. Epub 2006 Sep 6. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2007. PMID: 16950667 Review.
-
Inducible nitric oxide synthase in human diseases.Clin Exp Immunol. 1998 Aug;113(2):147-56. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1998.00648.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9717962 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Simvastatin prevents articular chondrocyte dedifferentiation induced by nitric oxide by inhibiting the expression of matrix metalloproteinases 1 and 13.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2018 Nov;243(15-16):1165-1172. doi: 10.1177/1535370218820650. Epub 2019 Jan 6. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2018. PMID: 32459510 Free PMC article.
-
Rituximab exerts its anti-arthritic effects via inhibiting NF-κB/GM-CSF/iNOS signaling in B cells in a mouse model of collagen-induced arthritis.Heliyon. 2023 May 25;9(6):e16673. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16673. eCollection 2023 Jun. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37274671 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress, vitamin e, and antioxidant capacity in knee osteoarthritis.J Clin Diagn Res. 2013 Sep;7(9):1855-9. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2013/5802.3333. Epub 2013 Sep 10. J Clin Diagn Res. 2013. PMID: 24179881 Free PMC article.
-
The evaluation of oxidative stress in osteoarthritis.Med Pharm Rep. 2020 Jan;93(1):12-22. doi: 10.15386/mpr-1422. Epub 2020 Jan 31. Med Pharm Rep. 2020. PMID: 32133442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of vitamin E on oxidative stress level in blood, synovial fluid, and synovial tissue in severe knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled study.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017 Jun 29;18(1):281. doi: 10.1186/s12891-017-1637-7. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017. PMID: 28662656 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Weyand CM, Goronzy JJ. T-cell responses in rheumatoid arthritis: systemic abnormalities – local disease. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 1999;11:210–7. - PubMed
-
- Yocum DE. Pathogenic cells and therapeutic targets in rheumatoid arthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1999;29:27–35. - PubMed
-
- Masi AT, Bijlsma JWJ, Chikanza IC, Pitzalis C, Cutolo M. Neuroendocrine, immunologic, and microvascular system interactions in rheumatoid arthritis: physiopathogenetic and therapeutic perspectives. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1999;29:65–81. - PubMed
-
- Edwards S, Hallet M. Seeing the wood for the trees: the forgotten role of neutrophils in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Today. 1997;18:320–4. - PubMed
-
- Pillinger MH, Abramson SB. The neutrophil in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1995;21:691–714. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

