Direct and efficient production of ethanol from cellulosic material with a yeast strain displaying cellulolytic enzymes
- PMID: 12324364
- PMCID: PMC126432
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.68.10.5136-5141.2002
Direct and efficient production of ethanol from cellulosic material with a yeast strain displaying cellulolytic enzymes
Abstract
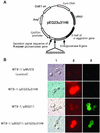
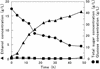
For direct and efficient ethanol production from cellulosic materials, we constructed a novel cellulose-degrading yeast strain by genetically codisplaying two cellulolytic enzymes on the cell surface of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. By using a cell surface engineering system based on alpha-agglutinin, endoglucanase II (EGII) from the filamentous fungus Trichoderma reesei QM9414 was displayed on the cell surface as a fusion protein containing an RGSHis6 (Arg-Gly-Ser-His(6)) peptide tag in the N-terminal region. EGII activity was detected in the cell pellet fraction but not in the culture supernatant. Localization of the RGSHis6-EGII-alpha-agglutinin fusion protein on the cell surface was confirmed by immunofluorescence microscopy. The yeast strain displaying EGII showed significantly elevated hydrolytic activity toward barley beta-glucan, a linear polysaccharide composed of an average of 1,200 glucose residues. In a further step, EGII and beta-glucosidase 1 from Aspergillus aculeatus No. F-50 were codisplayed on the cell surface. The resulting yeast cells could grow in synthetic medium containing beta-glucan as the sole carbon source and could directly ferment 45 g of beta-glucan per liter to produce 16.5 g of ethanol per liter within about 50 h. The yield in terms of grams of ethanol produced per gram of carbohydrate utilized was 0.48 g/g, which corresponds to 93.3% of the theoretical yield. This result indicates that efficient simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of cellulose to ethanol are carried out by a recombinant yeast cells displaying cellulolytic enzymes.
Figures


References
-
- Bayer, E. A., E. Morag, and R. Lamed. 1994. The cellulosome—a treasure-trove for biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol. 12:378-386. - PubMed
-
- Boder, E. T., and K. D. Wittrup. 1997. Yeast surface display for screening combinatorial polypeptide libraries. Nat. Biotechnol. 15:553-557. - PubMed
-
- Cho, K. M., Y. J. Yoo, and H. S. Kang. 1999. δ-Integration of endo/exo-glucanase and β-glucosidase genes into the yeast chromosomes for direct conversion of cellulose to ethanol. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 25:23-30.
-
- Dubois, M., K. A. Gilles, J. K. Hamilton, P. A. Reberse, and F. Smith. 1956. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 28:350-356.
-
- Henrissat, B., H. Driguez, C. Viet, and M. Schülein. 1985. Synergism of cellulases from Trichoderma reesei in the degradation of cellulose. Bio/Technology 3:722-726.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

