Group I metabotropic glutamate receptor signaling via Galpha q/Galpha 11 secures the induction of long-term potentiation in the hippocampal area CA1
- PMID: 12351712
- PMCID: PMC6757807
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-19-08379.2002
Group I metabotropic glutamate receptor signaling via Galpha q/Galpha 11 secures the induction of long-term potentiation in the hippocampal area CA1
Abstract
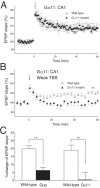
Heterotromeric G-proteins of the Gq family are thought to transduce signals from group I metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) in central neurons. We investigated roles of this cascade in hippocampal long-term potentiation (LTP) by using null-mutant mice lacking the alpha subunit of Gq (Galphaq) or G11 (Galpha11). We found no obvious abnormalities in the morphology, layer structure, expression of NMDA receptors, and basic parameters of excitatory synaptic transmission in the hippocampus of Galphaq mutant mice. We used theta burst stimulation (TBS) (3-10 burst trains at 5 Hz; each train consisted of five stimuli at 100 Hz) to induce LTP at Schaffer collateral to CA1 pyramidal cell synapses. Conventional TBS with 10 burst trains induced robust LTP in wild-type, Galphaq mutant, and Galpha11 mutant mice. Weak TBS with three burst trains consistently induced LTP in wild-type mice. In contrast, the same weak TBS was insufficient to induce LTP in Galphaq and Galpha11 mutant mice. In wild-type mice, the LTP by weak TBS was abolished by inhibiting group I mGluR or protein kinase C (PKC) but not by blocking muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Prior activation of group I mGluR by an agonist significantly enhanced the LTP by weak TBS in wild-type mice. However, this priming effect was absent in Galphaq mutant mice. These results indicate that the signaling from group I mGluR to PKC involving Galphaq/Galpha11 does not constitute the main pathway for LTP, but it secures LTP induction by lowering its threshold in the hippocampal area CA1.
Figures






Similar articles
-
G(alpha)q-deficient mice lack metabotropic glutamate receptor-dependent long-term depression but show normal long-term potentiation in the hippocampal CA1 region.J Neurosci. 2001 Jul 15;21(14):4943-8. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-14-04943.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11438569 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of Group II Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors Promotes LTP Induction at Schaffer Collateral-CA1 Pyramidal Cell Synapses by Priming NMDA Receptors.J Neurosci. 2016 Nov 9;36(45):11521-11531. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1519-16.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27911756 Free PMC article.
-
GABAB receptor- and metabotropic glutamate receptor-dependent cooperative long-term potentiation of rat hippocampal GABAA synaptic transmission.J Physiol. 2003 Nov 15;553(Pt 1):155-67. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.049015. Epub 2003 Sep 8. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12963794 Free PMC article.
-
Theta-burst LTP.Brain Res. 2015 Sep 24;1621:38-50. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.10.034. Epub 2014 Oct 27. Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25452022 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Muscarinic Receptors, from Synaptic Plasticity to its Role in Network Activity.Neuroscience. 2021 Feb 21;456:60-70. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2020.04.005. Epub 2020 Apr 8. Neuroscience. 2021. PMID: 32278062 Review.
Cited by
-
Hippocampal Protein Kinase C Signaling Mediates the Short-Term Memory Impairment Induced by Delta9-Tetrahydrocannabinol.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018 Apr;43(5):1021-1031. doi: 10.1038/npp.2017.175. Epub 2017 Aug 17. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018. PMID: 28816239 Free PMC article.
-
mGluR5 from Primary Sensory Neurons Promotes Opioid-Induced Hyperalgesia and Tolerance by Interacting with and Potentiating Synaptic NMDA Receptors.J Neurosci. 2023 Aug 2;43(31):5593-5607. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0601-23.2023. Epub 2023 Jul 14. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37451981 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of micro-opioid receptors in GABAergic synaptic transmission in the striosome and matrix compartments of the striatum.Mol Neurobiol. 2008 Apr-Jun;37(2-3):104-15. doi: 10.1007/s12035-008-8023-2. Epub 2008 May 13. Mol Neurobiol. 2008. PMID: 18473190 Review.
-
Activity bidirectionally regulates AMPA receptor mRNA abundance in dendrites of hippocampal neurons.J Neurosci. 2006 Aug 9;26(32):8339-51. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0472-06.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16899729 Free PMC article.
-
Forebrain-specific inactivation of Gq/G11 family G proteins results in age-dependent epilepsy and impaired endocannabinoid formation.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Aug;26(15):5888-94. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00397-06. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16847339 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abe T, Sugihara H, Nawa H, Shigemoto R, Mizuno N, Nakanishi S. Molecular characterization of a novel metabotropic glutamate receptor mGluR5 coupled to inositol phosphate/Ca2+ signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:13361–13368. - PubMed
-
- Abeliovich A, Chen C, Goda Y, Silvia AJ, Stevens CF, Tonegawa S. Modified hippocampal long-term potentiation in PKCγ mutant mice. Cell. 1993;75:1253–1262. - PubMed
-
- Abraham WC, Bear MF. Metaplasticity: the plasticity of synaptic plasticity. Trends Neurosci. 1996;19:126–130. - PubMed
-
- Auerbach JM, Segal M. A novel cholinergic induction of long-term potentiation in rat hippocampus. J Neurophysiol. 1994;72:2034–2040. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
