Thioltransferase (glutaredoxin) mediates recovery of motor neurons from excitotoxic mitochondrial injury
- PMID: 12351714
- PMCID: PMC6757782
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-19-08402.2002
Thioltransferase (glutaredoxin) mediates recovery of motor neurons from excitotoxic mitochondrial injury
Abstract
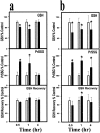
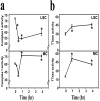
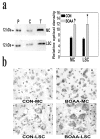
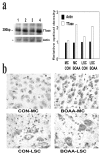
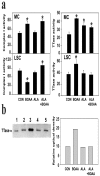
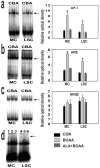
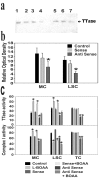
Mitochondrial dysfunction involving electron transport components is implicated in the pathogenesis of several neurodegenerative disorders and is a critical event in excitotoxicity. Excitatory amino acid L-beta-N-oxalylamino-L-alanine (L-BOAA), causes progressive corticospinal neurodegeneration in humans. In mice, L-BOAA triggers glutathione loss and protein thiol oxidation that disrupts mitochondrial complex I selectively in motor cortex and lumbosacral cord, the regions affected in humans. We examined the factors regulating postinjury recovery of complex I in CNS regions after a single dose of L-BOAA. The expression of thioltransferase (glutaredoxin), a protein disulfide oxidoreductase regulated through AP1 transcription factor was upregulated within 30 min of L-BOAA administration, providing the first evidence for functional regulation of thioltransferase during restoration of mitochondrial function. Regeneration of complex I activity in motor cortex was concurrent with increase in thioltransferase protein and activity, 1 hr after the excitotoxic insult. Pretreatment with alpha-lipoic acid, a thiol delivery agent that protects motor neurons from L-BOAA-mediated toxicity prevented the upregulation of thioltransferase and AP1 activation, presumably by maintaining thiol homeostasis. Downregulation of thioltransferase using antisense oligonucleotides prevented the recovery of complex I in motor cortex and exacerbated the mitochondrial dysfunction in lumbosacral cord, providing support for the critical role for thioltransferase in maintenance of mitochondrial function in the CNS.
Figures
References
-
- Akerboom TP, Sies H. Assay of glutathione, glutathione disulfide and glutathione mixed disulfides in biological samples. Methods Enzymol. 1981;77:373–382. - PubMed
-
- Annepu J, Ravindranath V. 1-Methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2, 3, 6 tetrahydropyridine induced complex I inhibition is reversed by disulfide reductant, dithiothreitol in mouse brain. Neurosci Lett. 2000;289:209–212. - PubMed
-
- Balijepalli S, Tirumalai PS, Swamy KV, Boyd MR, Mieyal JJ, Ravindranath V. Rat brain thioltransferase: regional distribution, immunological characterization and localization by fluorescent in situ hybridization. J Neurochem. 1999;72:1170–1178. - PubMed
-
- Balijepalli S, Boyd MR, Ravindranath V. Human brain thioltransferase: constitutive expression and localization by fluorescent in situ hybridization. Mol Brain Res. 2000;85:123–132. - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of dye-binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
