Structure/function analysis of Ca2+ binding to the C2A domain of synaptotagmin 1
- PMID: 12351718
- PMCID: PMC6757773
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-19-08438.2002
Structure/function analysis of Ca2+ binding to the C2A domain of synaptotagmin 1
Abstract
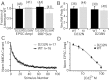
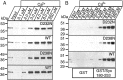
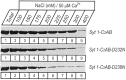
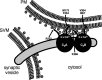
Synaptotagmin 1, a Ca2+ sensor for fast synaptic vesicle exocytosis, contains two C2 domains that form Ca2+-dependent complexes with phospholipids. To examine the functional importance of Ca2+ binding to the C2A domain of synaptotagmin 1, we studied two C2A domain mutations, D232N and D238N, using recombinant proteins and knock-in mice. Both mutations severely decreased intrinsic Ca2+ binding and Ca2+-dependent phospholipid binding by the isolated C2A domain. Both mutations, however, did not alter the apparent Ca2+ affinity of the double C2 domain fragment, although both decreased the tightness of the Ca2+/phospholipid/double C2 domain complex. When introduced into the endogenous synaptotagmin 1 gene in mice, the D232N and D238N mutations had no apparent effect on morbidity and mortality and caused no detectable alteration in the Ca2+-dependent properties of synaptotagmin 1. Electrophysiological recordings of cultured hippocampal neurons from knock-in mice revealed that neither mutation induced major changes in synaptic transmission. The D232N mutation, however, caused increased synaptic depression during repetitive stimulation, whereas the D238N mutation did not exhibit this phenotype. Our data indicate that Ca2+ binding to the C2A domain of synaptotagmin 1 may be important but not essential, consistent with the finding that the two C2 domains cooperate and may be partially redundant in Ca2+-dependent phospholipid binding. Moreover, although the apparent Ca2+ affinity of the synaptotagmin 1/phospholipid complex is critical, the tightness of the Ca2+/phospholipid complex is not. Our data also demonstrate that subtle changes in the biochemical properties of synaptotagmin 1 can result in significant alterations in synaptic responses.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mechanism of phospholipid binding by the C2A-domain of synaptotagmin I.Biochemistry. 1998 Sep 8;37(36):12395-403. doi: 10.1021/bi9807512. Biochemistry. 1998. PMID: 9730811
-
The C2A domain of synaptotagmin-like protein 3 (Slp3) is an atypical calcium-dependent phospholipid-binding machine: comparison with the C2A domain of synaptotagmin I.Biochem J. 2002 Sep 1;366(Pt 2):681-7. doi: 10.1042/BJ20020484. Biochem J. 2002. PMID: 12049610 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholipid composition dependence of Ca2+-dependent phospholipid binding to the C2A domain of synaptotagmin IV.J Biol Chem. 1996 Apr 5;271(14):8430-4. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.14.8430. J Biol Chem. 1996. PMID: 8626542
-
Role of synaptotagmin, a Ca2+ and inositol polyphosphate binding protein, in neurotransmitter release and neurite outgrowth.Chem Phys Lipids. 1999 Apr;98(1-2):59-67. doi: 10.1016/s0009-3084(99)00018-3. Chem Phys Lipids. 1999. PMID: 10358928 Review.
-
Synaptotagmin in Ca2+ -dependent exocytosis: dynamic action in a flash.Neuron. 2003 May 22;38(4):521-4. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(03)00290-3. Neuron. 2003. PMID: 12765604 Review.
Cited by
-
DOC2B, C2 domains, and calcium: A tale of intricate interactions.Mol Neurobiol. 2010 Feb;41(1):42-51. doi: 10.1007/s12035-009-8094-8. Epub 2010 Jan 7. Mol Neurobiol. 2010. PMID: 20052564 Review.
-
C2B polylysine motif of synaptotagmin facilitates a Ca2+-independent stage of synaptic vesicle priming in vivo.Mol Biol Cell. 2006 Dec;17(12):5211-26. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e06-07-0622. Epub 2006 Sep 20. Mol Biol Cell. 2006. PMID: 16987956 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and mutational analysis of functional differentiation between synaptotagmins-1 and -7.PLoS One. 2010 Sep 2;5(9):e12544. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012544. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20824061 Free PMC article.
-
The C2A domain of synaptotagmin is an essential component of the calcium sensor for synaptic transmission.PLoS One. 2020 Feb 7;15(2):e0228348. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228348. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32032373 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane-docking loops of the cPLA2 C2 domain: detailed structural analysis of the protein-membrane interface via site-directed spin-labeling.Biochemistry. 2003 Nov 18;42(45):13227-40. doi: 10.1021/bi035119+. Biochemistry. 2003. PMID: 14609334 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bai J, Earles CA, Lewis JL, Chapman ER. Membrane-embedded synaptotagmin penetrates cis or trans target membranes and clusters via a novel mechanism. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:25427–25435. - PubMed
-
- Bollmann JH, Sakmann B, Borst JG. Calcium sensitivity of glutamate release in a calyx-type terminal. Science. 2000;289:953–957. - PubMed
-
- Chapman ER, Davis AF. Direct interaction of a Ca2+-binding loop of synaptotagmin with lipid bilayers. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:13995–14001. - PubMed
-
- Chapman ER, Jahn R. Calcium-dependent interaction of the cytoplasmic region of synaptotagmin with membranes. Autonomous function of a single C2-homologous domain. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:5735–5741. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
