Cyclin-dependent kinase-2 controls oligodendrocyte progenitor cell cycle progression and is downregulated in adult oligodendrocyte progenitors
- PMID: 12351729
- PMCID: PMC6757806
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-19-08553.2002
Cyclin-dependent kinase-2 controls oligodendrocyte progenitor cell cycle progression and is downregulated in adult oligodendrocyte progenitors
Abstract
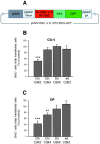
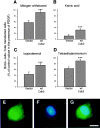
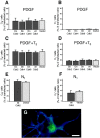
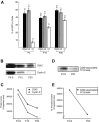
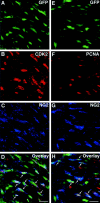
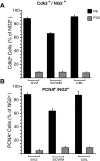
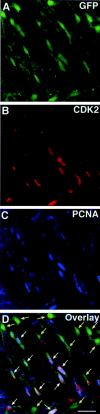
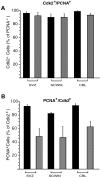
Proliferation of oligodendrocyte progenitor (OP) cells is a crucial process controlling myelination in the CNS. Previous studies demonstrated a correlation between OP proliferation rate and cyclin E/cyclin-dependent kinase-2 (cdk2) activity. To establish a causal link between cyclin E/cdk2 activity and OP proliferation, we selectively modulated cdk2 activity in vitro by transfection of cultured OP cells. Dominant-negative (Dn)-cdk2 overexpression inhibited mitogen-induced OP cell proliferation, whereas wild-type (wt)-cdk2 prevented cell cycle arrest caused by anti-mitotic signals. Dn-cdk2- or wt-cdk2-mediated regulation of G(1)/S transition, per se, did not influence initiation of OP differentiation. To study the function of cyclin E/cdk2 in OP cells during development in vivo, we analyzed cdk2 and cyclin E expression in cells acutely isolated from transgenic mice expressing the green fluorescent protein (GFP) under the control of the 2'-3'-cyclic nucleotide 3'-phosphodiesterase gene promoter. Both cyclin E/cdk2 protein levels and activity were decreased in GFP(+) oligodendrocyte lineage cells between postnatal days 4 and 30. Immunostaining of NG2(+)/GFP(+) OP cells in brain tissue sections showed a 90% decrease in overall cell proliferation and cdk2 expression between perinatal and adult cells. However, cdk2 expression within the proliferating (i.e., expressing the proliferating cell nuclear antigen) OP cell population was maintained throughout development. Our data indicate that: (1) cyclin E/cdk2 activity plays a pivotal function in OP cell cycle decisions occurring at G(1)/S checkpoint; (2) initiation of OP differentiation is independent of cyclinE/cdk2 checkpoint, and (3) intrinsic differences in cyclin E/cdk2 expression and activity may underlie the slowly proliferative state that characterizes so-called "quiescent" adult OP cells in vivo.
Figures
References
-
- Belachew S, Yuan X, Gallo V. Unraveling oligodendrocyte origin and function by cell-specific transgenesis. Dev Neurosci. 2001;23:287–298. - PubMed
-
- Bergles DE, Roberts JD, Somogyi P, Jahr CE. Glutamatergic synapses on oligodendrocyte precursor cells in the hippocampus. Nature. 2000;405:187–191. - PubMed
-
- Calver AR, Hall AC, Yu WP, Walsh FS, Heath JK, Betsholtz C, Richardson WD. Oligodendrocyte population dynamics and the role of PDGF in vivo. Neuron. 1998;20:869–882. - PubMed
-
- Chan CL, Wigley CB, Berry M. Oligodendrocyte-type 2 astrocyte (O-2A) progenitor cells from neonatal and adult rat optic nerve differ in their responsiveness to platelet-derived growth factor. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1990;55:275–282. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
