Responses of neurons in cat primary auditory cortex to bird chirps: effects of temporal and spectral context
- PMID: 12351736
- PMCID: PMC6757805
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-19-08619.2002
Responses of neurons in cat primary auditory cortex to bird chirps: effects of temporal and spectral context
Abstract
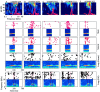
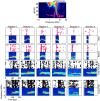
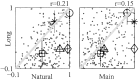
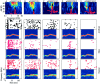
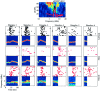
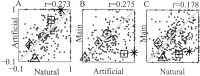
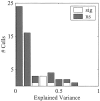
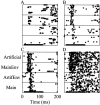
The responses of neurons to natural sounds and simplified natural sounds were recorded in the primary auditory cortex (AI) of halothane-anesthetized cats. Bird chirps were used as the base natural stimuli. They were first presented within the original acoustic context (at least 250 msec of sounds before and after each chirp). The first simplification step consisted of extracting a short segment containing just the chirp from the longer segment. For the second step, the chirp was cleaned of its accompanying background noise. Finally, each chirp was replaced by an artificial version that had approximately the same frequency trajectory but with constant amplitude. Neurons had a wide range of different response patterns to these stimuli, and many neurons had late response components in addition, or instead of, their onset responses. In general, every simplification step had a substantial influence on the responses. Neither the extracted chirp nor the clean chirp evoked a similar response to the chirp presented within its acoustic context. The extracted chirp evoked different responses than its clean version. The artificial chirps evoked stronger responses with a shorter latency than the corresponding clean chirp because of envelope differences. These results illustrate the sensitivity of neurons in AI to small perturbations of their acoustic input. In particular, they pose a challenge to models based on linear summation of energy within a spectrotemporal receptive field.
Figures
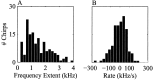
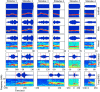
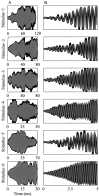
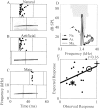
References
-
- Brosch M, Schreiner CE. Time course of forward masking tuning curves in cat primary auditory cortex. J Neurophysiol. 1997;77:923–943. - PubMed
-
- Brugge JF, Reale RA, Hind JE. Spatial receptive fields of primary auditory cortical neurons in quiet and in the presence of continuous background noise. J Neurophysiol. 1998;80:2417–2432. - PubMed
-
- Calford MB, Semple MN. Monaural inhibition in cat auditory cortex. J Neurophysiol. 1995;73:1876–1891. - PubMed
-
- Calhoun BM, Schreiner CE. Spectral envelope coding in cat primary auditory cortex: linear and non-linear effects of stimulus characteristics. Eur J Neurosci. 1998;10:926–940. - PubMed
-
- deCharms RC, Blake DT, Merzenich MM. Optimizing sound features for cortical neurons. Science. 1998;280:1439–1443. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
