Mutation of the alpha2A-adrenoceptor impairs working memory performance and annuls cognitive enhancement by guanfacine
- PMID: 12351753
- PMCID: PMC6757781
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-19-08771.2002
Mutation of the alpha2A-adrenoceptor impairs working memory performance and annuls cognitive enhancement by guanfacine
Abstract
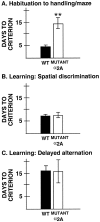
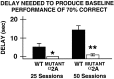
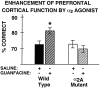
Norepinephrine strengthens the working memory, behavioral inhibition, and attentional functions of the prefrontal cortex through actions at postsynaptic alpha2-adrenoceptors (alpha2-AR). The alpha2-AR agonist guanfacine enhances prefrontal cortical functions in rats, monkeys, and human beings and ameliorates prefrontal cortical deficits in patients with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. The present study examined the subtype of alpha2-AR underlying these beneficial effects. Because there are no selective alpha2A-AR, alpha2B-AR, or alpha2C-AR agonists or antagonists, genetically altered mice were used to identify the molecular target of the action of guanfacine. Mice with a point mutation of the alpha2A-AR, which serves as a functional knock-out, were compared with wild-type animals and with previously published studies of alpha2C-AR knock-out mice (Tanila et al., 1999). Mice were adapted to handling on a T maze and trained on either a spatial delayed alternation task that is sensitive to prefrontal cortical damage or a spatial discrimination control task with similar motor and motivational demands but no dependence on prefrontal cortex. The effects of guanfacine on performance of the delayed alternation task were assessed in additional groups of wild-type versus alpha2A-AR mutant mice. We observed that functional loss of the alpha2A-AR subtype, unlike knock-out of the alpha2C-AR subtype, weakened performance of the prefrontal cortical task without affecting learning and resulted in loss of the beneficial response to guanfacine. These data demonstrate the importance of alpha2A-AR subtype stimulation for the cognitive functions of the prefrontal cortex and identify the molecular substrate for guanfacine and novel therapeutic interventions.
Figures
References
-
- Aoki C, Go C-G, Venkatesan C, Kurose H. Perikaryal and synaptic localization of alpha-2A-adrenergic receptor-like immunoreactivity. Brain Res. 1994;650:181–204. - PubMed
-
- Arnsten AFT, Contant TA. Alpha-2 adrenergic agonists decrease distractability in aged monkeys performing a delayed response task. Psychopharmacology. 1992;108:159–169. - PubMed
-
- Arnsten AFT, Goldman-Rakic PS. Alpha-2 adrenergic mechanisms in prefrontal cortex associated with cognitive decline in aged nonhuman primates. Science. 1985;230:1273–1276. - PubMed
-
- Arnsten AFT, Goldman-Rakic PS. Analysis of alpha-2 adrenergic agonist effects on the delayed nonmatch-to-sample performance of aged rhesus monkeys. Neurobiol Aging. 1990;11:583–590. - PubMed
-
- Arnsten AFT, Leslie FM. Behavioral and receptor binding analysis of the alpha-2 adrenergic agonist, UK-14304 (5 bromo-6 [2-imidazoline-2-yl amino] quinoxaline): evidence for cognitive enhancement at an alpha-2 adrenoceptor subtype. Neuropharmacology. 1991;30:1279–1289. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
