Monitoring drug resistance in chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV)-infected patients during lamivudine therapy: evaluation of performance of INNO-LiPA HBV DR assay
- PMID: 12354872
- PMCID: PMC130856
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.40.10.3729-3734.2002
Monitoring drug resistance in chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV)-infected patients during lamivudine therapy: evaluation of performance of INNO-LiPA HBV DR assay
Abstract
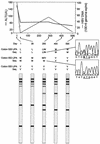
Sensitive and early detection of emerging hepatitis B virus (HBV) drug resistance may not only help monitor the viral dynamics associated with lamivudine treatment but could also improve therapeutic decision making. This is especially important when new antivirals effective against lamivudine-resistant HBV become available. A total of 159 serum samples from 33 chronic HBV patients receiving lamivudine treatment were analyzed at four centers for the presence of lamivudine-resistant mutations at codons 528 [180] (proposed revised nomenclature according to Stuyver et al. [Hepatology 33:751-757, 2001] shown in brackets), 552 [204], and 555 [207] of the HBV polymerase. Sequencing data were compared with results generated by the INNO-LiPA HBV DR line probe assay (LiPA), an assay based on reverse hybridization of amplified HBV DNA fragments with specific nucleotide probes immobilized on nitrocellulose strips. LiPA provided at least the same information as sequencing for 97.5% of all codons analyzed for codon 528 [180], 95% for codon 552 [204], and 100% for codon 555 [207]. The most common reason for discrepant or indeterminate results (0.4% and 1.5%, respectively) in a small percentage of the population tested could be attributed to polymorphisms not yet covered by LiPA probes. In at least five patients, a mutant could be detected earlier by LiPA than by sequencing. In 15 patients, LiPA detected mixed wild-type and mutant virus populations before viral breakthrough. These results demonstrate that INNO-LiPA HBV DR is a highly sensitive and easily applicable assay for the detection and monitoring of lamivudine-resistant mutations in chronic hepatitis B patients and that the assay is more sensitive than sequencing in detecting mixed mutant and wild-type sequences.
Figures
References
-
- Aberle, S. W., J. Kletzmayr, B. Watschnger, B. Schmied, N. Vetter, and E. Puchhammer-Stöckl. 2001. Comparison of sequence analysis and the INNO-LiPA HBV DR line probe assay for detection of lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B virus strains in patients under various clinical conditions. J. Clin. Microbiol. 39:1972-1974. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aye, T. T., A. I. Barthelomeusz, T. Shaw, A. Breshkin, L. Gronen, S. Bowden, J. McMillan, and S. Locarnini. 1996. Hepatitis B virus polymerase mutations during famciclovir therapy in patients following liver transplantation. Hepatology 24(Suppl.):285A. - PubMed
-
- Aye, T. T., A. I. Barthelomeusz, T. Shaw, S. Bowden, A. Breshkin, J. McMillan, P. Angus, and S. Locarnini. 1997. Hepatitis B virus polymerase mutations during antiviral therapy in a patient following liver transplantation. J. Hepatol. 26:1148-1153. - PubMed
-
- Benhamou, Y., M. Bochet, V. Thibault, V. Calvez, M. H. Fievet, P. Vig, G. C. Gibbs, C. Brosgard, J. Fry, H. Namini, C. Katlama, and T. Poynard. 2001. Safety and efficacy of adefovir dipivoxil in patients co-infected with human immunodeficiency virus-1 and lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B virus: an open label study. Lancet 358:718-723. - PubMed
-
- Chayama, K., Y. Suzuki, M. Kobayashi, M. Kobayashi, A. Tsubota, M. Hashimoto, Y. Miyano, H. Koike, M. Kobayashi, I. Koida, Y. Arase, S. Saitoh, N. Murashima, K. Ikeda, and H. Kumada. 1998. Emergence and takeover of YMDD motif mutant hepatitis B virus during long-term lamivudine therapy and re-takeover by wild type after cessation of therapy. Hepatology 27:1711-1716. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

