Evaluation of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with recombinant rhoptry-associated protein 1 antigen against Babesia bovis for the detection of specific antibodies in cattle
- PMID: 12354879
- PMCID: PMC130890
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.40.10.3771-3775.2002
Evaluation of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with recombinant rhoptry-associated protein 1 antigen against Babesia bovis for the detection of specific antibodies in cattle
Abstract
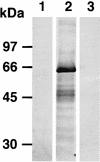
The gene encoding Babesia bovis rhoptry-associated protein 1 (RAP-1) was used to develop an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) to measure specific antibodies against B. bovis. The B. bovis RAP-1 gene was subcloned into a baculovirus transfer vector, and the RAP-1 protein was expressed in insect cells infected with a recombinant baculovirus. The recombinant B. bovis RAP-1 of 65 kDa was detected with anti-RAP-1 mouse serum by Western blotting, and this recombinant RAP-1 was used as an antigen in the ELISA. The ELISA was able to differentiate between B. bovis-infected sera and B. bigemina-infected sera or noninfected normal bovine sera. The results demonstrate that the recombinant RAP-1 expressed in insect cells might be a useful antigen for the detection of antibodies to B. bovis.
Figures



References
-
- Avarazed, A., D. T. de Waal, I. Igarashi, A. Saito, T. Oyamada, Y. Toyoda, and N. Suzuki. 1997. Prevalence of equine piroplasmosis in central Mongolia. Ondersterpoort J. Vet. Res. 64:141-145. - PubMed
-
- Bose, R., W. K. Jorgensen, R. J. Dalgliesh, K. T. Friedhoff, and A. J. de Vos. 1995. Current state and future trends in diagnosis of babesiosis. Vet. Parasitol. 57:61-74. - PubMed
-
- Brown, W. C., and G. H. Palmer. 1999. Designing a blood-stage vaccine against Babesia bovis and B. bigemina. Parasitol. Today 15:275-281. - PubMed
-
- Brown, W. C., T. F. McElwain, B. J. Ruef, C. E. Suraez, V. Shkap, C. G. Chitko-Mckown, W. Tuo, A. C. Riece-Ficht, and G. H. Palmer. 1996. Babesia bovis: rhoptry-associated protein 1 is immunodominant for T helper cell epitopes conserved among geographically distant B. bovis strains. Infect. Immun. 64:3341-3350. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

