Use of 16S rRNA gene sequencing for identification of nonfermenting gram-negative bacilli recovered from patients attending a single cystic fibrosis center
- PMID: 12354883
- PMCID: PMC130867
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.40.10.3793-3797.2002
Use of 16S rRNA gene sequencing for identification of nonfermenting gram-negative bacilli recovered from patients attending a single cystic fibrosis center
Abstract
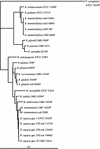
During 1999, we used partial 16S rRNA gene sequencing for the prospective identification of atypical nonfermenting gram-negative bacilli isolated from patients attending our cystic fibrosis center. Of 1,093 isolates of nonfermenting gram-negative bacilli recovered from 148 patients, 46 (4.2%) gave problematic results with conventional phenotypic tests. These 46 isolates were genotypically identified as Pseudomonas aeruginosa (19 isolates, 12 patients), Achromobacter xylosoxidans (10 isolates, 8 patients), Stenotrophomonas maltophilia (9 isolates, 9 patients), Burkholderia cepacia genomovar I/III (3 isolates, 3 patients), Burkholderia vietnamiensis (1 isolate), Burkholderia gladioli (1 isolate), and Ralstonia mannitolilytica (3 isolates, 2 patients), a recently recognized species.
Figures
References
-
- Burdge, D. R., M. A. Noble, M. E. Campbell, V. L. Krell, and D. P. Speert. 1995. Xanthomonas maltophilia misidentified as Pseudomonas cepacia in cultures of sputum from patients with cystic fibrosis: a diagnostic pitfall with major clinical implications. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2:445-448. - PubMed
-
- Burns, J. L., J. Emerson, J. R. Stapp, D. L. Yim, Y. J. Krzewinski, L. Louden, B. W. Ramsey, and C. R. Clausen. 1998. Microbiology of sputum from patients at cystic fibrosis centers in the United States. Clin. Infect. Dis. 27:158-163. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases