DNA differential diagnosis of human taeniid cestodes by base excision sequence scanning thymine-base reader analysis with mitochondrial genes
- PMID: 12354889
- PMCID: PMC130864
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.40.10.3818-3821.2002
DNA differential diagnosis of human taeniid cestodes by base excision sequence scanning thymine-base reader analysis with mitochondrial genes
Abstract
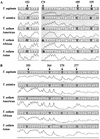
For DNA differential diagnosis of human Taenia cestodes, a base excision sequence scanning thymine-base method using the cytochrome c oxidase subunit I and cytochrome b genes as targets was used. The characteristic thymine-base peak profiles provide four distinct types, unique for T. saginata, T. asiatica, and two genotypes of T. solium. This approach provides a useful tool for the identification and diagnosis of human taeniid cestodes without DNA sequencing if nucleotide sequence databases are available.
Figures
References
-
- Bowles, J., and D. P. McManus. 1994. Genetic characterization of the Asian Taenia, a newly described taeniid cestode of humans. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 50:33-44. - PubMed
-
- Brieger, J., E. J. Weidt, K. Gansen, and H. J. Decker. 1999. Detection of a novel germline mutation in the von Hippel-Lindau tumor-suppressor gene by fluorescence-labelled base excision sequence scanning (F-BESS). Clin. Chem. 45:1564-1567. - PubMed
-
- Earnest, M. P., L. B. Reller, C. M. Filley, and A. J. Grek. 1987. Neurocysticercosis in the United States: 35 cases and a review. Rev. Infect. Dis. 9:961-979. - PubMed
-
- Fan, P. C. 1989. Taiwan Taenia and taeniasis. Parasitol. Today 4:86-88. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

