Use of spoligotyping for accurate classification of recurrent tuberculosis
- PMID: 12354898
- PMCID: PMC130897
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.40.10.3851-3853.2002
Use of spoligotyping for accurate classification of recurrent tuberculosis
Abstract
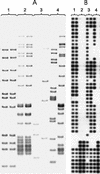
The spoligotyping method has become an important tool for the tracking of Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains in different epidemiological settings. In this study, we demonstrate the ability of the spoligotyping technique to accurately determine the pathogenetic mechanism of recurrent disease. This methodology has advantages over conventional restriction fragment length polymorphism methods which may be useful in large-scale intervention studies.
Figures
References
-
- Corbett, E. L., G. J. Churchyard, T. Clayton, P. Herselman, B. Williams, R. Hayes, D. Mulder, and K. M. De Cock. 1999. Risk factors for pulmonary mycobacterial disease in South African gold miners. A case-control study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 159:94-99. - PubMed
-
- Cronin, W. A., J. E. Golub, L. S. Magder, N. G. Baruch, M. J. Lathan, L. N. Mukasa, N. Hooper, J. H. Razeq, D. Mulcahy, W. H. Benjamin, and W. R. Bishai. 2001. Epidemiologic usefulness of spoligotyping for secondary typing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates with low copy numbers of IS6110. J. Clin. Microbiol. 39: 3709-3711. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

