A computerized model for the self-non-self discrimination at the level of the T(h) (Th genesis). I. The origin of 'primer' effector T(h) cells
- PMID: 12356676
- PMCID: PMC1360151
- DOI: 10.1093/intimm/dxf078
A computerized model for the self-non-self discrimination at the level of the T(h) (Th genesis). I. The origin of 'primer' effector T(h) cells
Abstract
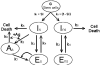
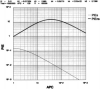
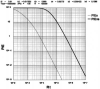
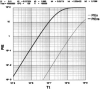
The ability of the immune system to respond by ridding a pathogen without debilitating the host depends upon the ability of the effector T(h) (eT(h)) to make a discrimination between 'self' and 'non-self' antigens. This ability is somatically learned and involves the sorting of the somatically generated random repertoire of initial state T(h) (iT(h)) into two classes of specificity: one, anti-self, the functional expression of which must be inactivated; the other, anti-non-self, the functional expression of which must be activated. We propose a model for the origin of a sufficiency of eT(h) anti-non-self and an insufficiency of eT(h) anti-self based on two postulates. (i) An antigen-independent pathway to a priming level of eT(h) anti-non-self under conditions where iT(h) anti-self are effectively deleted by interaction with self. This state is established during a window of fetal development and maintained throughout life because self is persistent. (ii) Associative recognition of antigen (peptide-MHC class II) on an antigen-presenting cell between iT(h) and 'primer' eT(h) that results in the rapid induction of an effective level of helper activity to non-self antigen. A computer simulation is provided that enables evaluation of this model.
Figures

References
-
- Langman RE, editor. Self—non-self discrimination revisited. Semin. Immunol. 2000;12:344. - PubMed
-
- Langman RE, Cohn M. A minimal model for the self— non-self discrimination: a return to the basics. Semin. Immunol. 2000;13:189. - PubMed
-
- Langman RE, Cohn M. The E—T (elephant—tadpole) paradox necessitates the concept of a unit of B-cell function: the Protecton. Mol. Immunol. 1987;24:675. - PubMed
-
- Cohn M, Langman RE. The Protecton: the evolutionarily selected unit of humoral immunity. Immunol. Rev. 1990;115:1. - PubMed
-
- Cohn M. A new concept of immune specificity emerges from a consideration of the self—non-self discrimination. Cell. Immunol. 1997;181:103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

