Requirement of N-glycan on GPI-anchored proteins for efficient binding of aerolysin but not Clostridium septicum alpha-toxin
- PMID: 12356721
- PMCID: PMC129030
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdf508
Requirement of N-glycan on GPI-anchored proteins for efficient binding of aerolysin but not Clostridium septicum alpha-toxin
Abstract
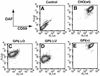
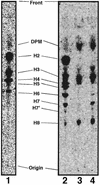
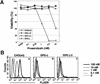
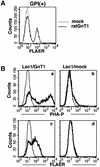
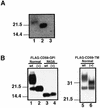
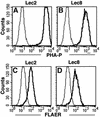
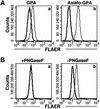
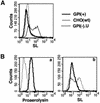
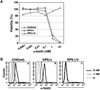
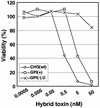
Aerolysin of the Gram-negative bacterium Aeromonas hydrophila consists of small (SL) and large (LL) lobes. The alpha-toxin of Gram-positive Clostridium septicum has a single lobe homologous to LL. These toxins bind to glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored proteins and generate pores in the cell's plasma membrane. We isolated CHO cells resistant to aerolysin, with the aim of obtaining GPI biosynthesis mutants. One mutant unexpectedly expressed GPI-anchored proteins, but nevertheless bound aerolysin poorly and was 10-fold less sensitive than wild-type cells. A cDNA of N-acetylglucosamine transferase I (GnTI) restored the binding of aerolysin to this mutant. Therefore, N-glycan is involved in the binding. Removal of mannoses by alpha-mannosidase II was important for the binding of aerolysin. In contrast, the alpha-toxin killed GnTI-deficient and wild-type CHO cells equally, indicating that its binding to GPI-anchored proteins is independent of N-glycan. Because SL bound to wild-type but not to GnTI-deficient cells, and because a hybrid toxin consisting of SL and the alpha-toxin killed wild-type cells 10-fold more efficiently than GnTI- deficient cells, SL with its binding site for N-glycan contributes to the high binding affinity of aerolysin.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Use of Clostridium septicum alpha toxins for isolation of various glycosylphosphatidylinositol-deficient cells.J Microbiol. 2005 Jun;43(3):266-71. J Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15995645
-
Generation and characterization of Clostridium septicum alpha toxin mutants and their use in diagnosing paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004 Nov 12;324(2):753-60. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.09.104. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004. PMID: 15474491
-
New mutant Chinese hamster ovary cell representing an unknown gene for attachment of glycosylphosphatidylinositol to proteins.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005 Oct 7;335(4):1060-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.07.177. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005. PMID: 16102723
-
Aerolysin from Aeromonas hydrophila and related toxins.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2001;257:35-52. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-56508-3_3. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11417121 Review. No abstract available.
-
Surface dynamics of aerolysin on the plasma membrane of living cells.Int J Med Microbiol. 2000 Oct;290(4-5):363-7. doi: 10.1016/S1438-4221(00)80042-9. Int J Med Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 11111912 Review.
Cited by
-
Sensitivity of polarized epithelial cells to the pore-forming toxin aerolysin.Infect Immun. 2003 Feb;71(2):739-46. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.2.739-746.2003. Infect Immun. 2003. PMID: 12540553 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular assembly of the aerolysin pore reveals a swirling membrane-insertion mechanism.Nat Chem Biol. 2013 Oct;9(10):623-9. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1312. Epub 2013 Aug 4. Nat Chem Biol. 2013. PMID: 23912165
-
Piercing Fishes: Porin Expansion and Adaptation to Hematophagy in the Vampire Snail Cumia reticulata.Mol Biol Evol. 2018 Nov 1;35(11):2654-2668. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msy156. Mol Biol Evol. 2018. PMID: 30099551 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of a cytocidal protein from lamprey and its mechanism of action in the selective killing of cancer cells.Cell Commun Signal. 2019 May 27;17(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s12964-019-0358-y. Cell Commun Signal. 2019. PMID: 31133022 Free PMC article.
-
Pore-forming activity of alpha-toxin is essential for clostridium septicum-mediated myonecrosis.Infect Immun. 2009 Mar;77(3):943-51. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01267-08. Epub 2009 Jan 12. Infect Immun. 2009. PMID: 19139192 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abrami L., Fivaz,M. and van der Goot,F.G. (2000) Adventures of a pore-forming toxin at the target cell surface. Trends Microbiol., 8, 168–172. - PubMed
-
- Abrami L., Fivaz,M., Kobayashi,T., Kinoshita,T., Parton,R.G. and van der Goot,F.G. (2001) Cross-talk between caveolae and glycosyl phosphatidylinositol-rich domains. J. Biol. Chem., 276, 30729–30736. - PubMed
-
- Abrami L., Velluz,M.C., Hong,Y., Ohishi,K., Mehlert,A., Ferguson,M., Kinoshita,T. and van der Goot,G.F. (2002) The glycan core of GPI-anchored proteins modulates aerolysin binding but is not sufficient: the polypeptide moiety is required for the toxin–receptor interaction. FEBS Lett., 512, 249–254. - PubMed
-
- Aebi M. and Hennet,T. (2001) Congenital disorders of glycosylation: genetic model systems lead the way. Trends Cell Biol., 11, 136–141. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

