Requirement of N-glycan on GPI-anchored proteins for efficient binding of aerolysin but not Clostridium septicum alpha-toxin
- PMID: 12356721
- PMCID: PMC129030
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdf508
Requirement of N-glycan on GPI-anchored proteins for efficient binding of aerolysin but not Clostridium septicum alpha-toxin
Abstract
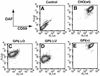
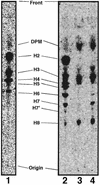
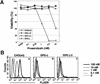
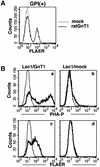
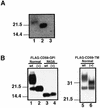
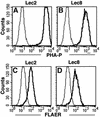
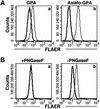
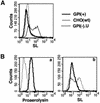
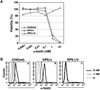
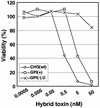
Aerolysin of the Gram-negative bacterium Aeromonas hydrophila consists of small (SL) and large (LL) lobes. The alpha-toxin of Gram-positive Clostridium septicum has a single lobe homologous to LL. These toxins bind to glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored proteins and generate pores in the cell's plasma membrane. We isolated CHO cells resistant to aerolysin, with the aim of obtaining GPI biosynthesis mutants. One mutant unexpectedly expressed GPI-anchored proteins, but nevertheless bound aerolysin poorly and was 10-fold less sensitive than wild-type cells. A cDNA of N-acetylglucosamine transferase I (GnTI) restored the binding of aerolysin to this mutant. Therefore, N-glycan is involved in the binding. Removal of mannoses by alpha-mannosidase II was important for the binding of aerolysin. In contrast, the alpha-toxin killed GnTI-deficient and wild-type CHO cells equally, indicating that its binding to GPI-anchored proteins is independent of N-glycan. Because SL bound to wild-type but not to GnTI-deficient cells, and because a hybrid toxin consisting of SL and the alpha-toxin killed wild-type cells 10-fold more efficiently than GnTI- deficient cells, SL with its binding site for N-glycan contributes to the high binding affinity of aerolysin.
Figures


References
-
- Abrami L., Fivaz,M. and van der Goot,F.G. (2000) Adventures of a pore-forming toxin at the target cell surface. Trends Microbiol., 8, 168–172. - PubMed
-
- Abrami L., Fivaz,M., Kobayashi,T., Kinoshita,T., Parton,R.G. and van der Goot,F.G. (2001) Cross-talk between caveolae and glycosyl phosphatidylinositol-rich domains. J. Biol. Chem., 276, 30729–30736. - PubMed
-
- Abrami L., Velluz,M.C., Hong,Y., Ohishi,K., Mehlert,A., Ferguson,M., Kinoshita,T. and van der Goot,G.F. (2002) The glycan core of GPI-anchored proteins modulates aerolysin binding but is not sufficient: the polypeptide moiety is required for the toxin–receptor interaction. FEBS Lett., 512, 249–254. - PubMed
-
- Aebi M. and Hennet,T. (2001) Congenital disorders of glycosylation: genetic model systems lead the way. Trends Cell Biol., 11, 136–141. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

