Binding of the PX domain of p47(phox) to phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate and phosphatidic acid is masked by an intramolecular interaction
- PMID: 12356722
- PMCID: PMC129041
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdf519
Binding of the PX domain of p47(phox) to phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate and phosphatidic acid is masked by an intramolecular interaction
Abstract
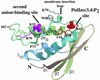
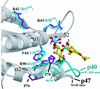
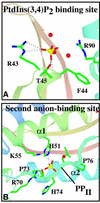
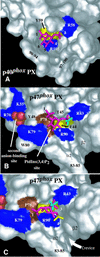
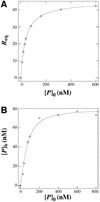
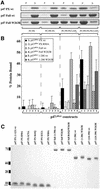
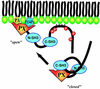
p47(phox) is a key cytosolic subunit required for activation of phagocyte NADPH oxidase. The X-ray structure of the p47(phox) PX domain revealed two distinct basic pockets on the membrane-binding surface, each occupied by a sulfate. These two pockets have different specificities: one preferentially binds phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate [PtdIns(3,4)P(2)] and is analogous to the phophatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PtdIns3P)-binding pocket of p40(phox), while the other binds anionic phospholipids such as phosphatidic acid (PtdOH) or phosphatidylserine. The preference of this second site for PtdOH may be related to previously observed activation of NADPH oxidase by PtdOH. Simultaneous occupancy of the two phospholipid-binding pockets radically increases membrane affinity. Strikingly, measurements for full-length p47(phox) show that membrane interaction by the PX domain is masked by an intramolecular association with the C-terminal SH3 domain (C-SH3). Either a site-specific mutation in C-SH3 (W263R) or a mimic of the phosphorylated form of p47(phox) [Ser(303, 304, 328, 359, 370)Glu] cause a transition from a closed to an open conformation that binds membranes with a greater affinity than the isolated PX domain.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Membrane binding mechanisms of the PX domains of NADPH oxidase p40phox and p47phox.J Biol Chem. 2003 Apr 18;278(16):14469-79. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M212579200. Epub 2003 Jan 29. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12556460
-
Phosphorylation of p47phox directs phox homology domain from SH3 domain toward phosphoinositides, leading to phagocyte NADPH oxidase activation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Apr 15;100(8):4474-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0735712100. Epub 2003 Apr 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12672956 Free PMC article.
-
Properties of phagocyte NADPH oxidase p47-phox mutants with unmasked SH3 (Src homology 3) domains: full reconstitution of oxidase activity in a semi-recombinant cell-free system lacking arachidonic acid.Biochem J. 2003 Jul 1;373(Pt 1):221-9. doi: 10.1042/BJ20021629. Biochem J. 2003. PMID: 12650641 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions between the components of the human NADPH oxidase: intrigues in the phox family.J Lab Clin Med. 1996 Nov;128(5):461-76. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2143(96)90043-8. J Lab Clin Med. 1996. PMID: 8900289 Review.
-
The PX domain: a new phosphoinositide-binding module.J Cell Sci. 2002 Mar 15;115(Pt 6):1099-105. doi: 10.1242/jcs.115.6.1099. J Cell Sci. 2002. PMID: 11884510 Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-Functional MPT Protein as a Therapeutic Agent against Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Biomedicines. 2021 May 13;9(5):545. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9050545. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34068051 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of NADPH oxidases in skeletal muscle.Free Radic Biol Med. 2016 Sep;98:18-28. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.05.011. Epub 2016 May 13. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016. PMID: 27184955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phospholipase dalpha1 and phosphatidic acid regulate NADPH oxidase activity and production of reactive oxygen species in ABA-mediated stomatal closure in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2009 Aug;21(8):2357-77. doi: 10.1105/tpc.108.062992. Epub 2009 Aug 18. Plant Cell. 2009. PMID: 19690149 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory functions of phospholipase D and phosphatidic acid in plant growth, development, and stress responses.Plant Physiol. 2005 Oct;139(2):566-73. doi: 10.1104/pp.105.068809. Plant Physiol. 2005. PMID: 16219918 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Membrane-Associated Proteins in Giardia lamblia.Genes (Basel). 2018 Aug 10;9(8):404. doi: 10.3390/genes9080404. Genes (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30103435 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ago T., Nunoi,H., Ito,T. and Sumimoto,H. (1999) Mechanism for phosphorylation-induced activation of the phagocyte NADPH oxidase protein p47phox. J. Biol. Chem., 274, 33644–33653. - PubMed
-
- Ago T., Takeya,R., Hiroaki,H., Kuribayashi,F., Ito,T., Kohda,D. and Sumimoto,H. (2001) The PX domain as a novel phosphoinositide-binding module. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 287, 733–738. - PubMed
-
- Babior B.M. (1999) NADPH oxidase: an update. Blood, 93, 1464–1476. - PubMed
-
- Bittova L., Stahelin,R.V. and Cho,W. (2001) Roles of ionic residues of the C1 domain in protein kinase C-α activation and the origin of phosphatidylserine specificity. J. Biol. Chem., 276, 4218–4226. - PubMed
-
- Bravo J. et al. (2001) The crystal structure of the PX domain from p40phox bound to phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate. Mol. Cell, 8, 829–839. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

