Conversion of PtdIns(4,5)P(2) into PtdIns(5)P by the S.flexneri effector IpgD reorganizes host cell morphology
- PMID: 12356723
- PMCID: PMC129044
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdf522
Conversion of PtdIns(4,5)P(2) into PtdIns(5)P by the S.flexneri effector IpgD reorganizes host cell morphology
Abstract
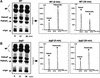
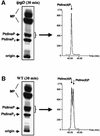
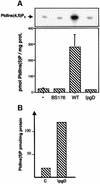
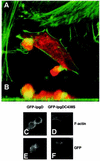
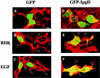
Phosphoinositides play a central role in the control of several cellular events including actin cytoskeleton organization. Here we show that, upon infection of epithelial cells with the Gram-negative pathogen Shigella flexneri, the virulence factor IpgD is translocated directly into eukaryotic cells and acts as a potent inositol 4-phosphatase that specifically dephosphorylates phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate [PtdIns(4,5)P(2)] into phosphatidylinositol 5-monophosphate [PtdIns(5)P] that then accumulates. Transfection experiments indicate that the transformation of PtdIns(4,5)P(2) into PtdIns(5)P by IpgD is responsible for dramatic morphological changes of the host cell, leading to a decrease in membrane tether force associated with membrane blebbing and actin filament remodelling. These data provide the molecular basis for a new mechanism employed by a pathogenic bacterium to promote membrane ruffling at the entry site.
Figures


References
-
- Bligh E.G. and Dyer,W.J. (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol., 37, 911–919. - PubMed
-
- Blondeau F., Laporte,J., Bodin,S., Superti-Furga,G., Payrastre,B. and Mandel,J.L. (2000) Myotubularin, a phosphatase deficient in myotubular myopathy, acts on phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate pathway. Hum. Mol. Genet., 9, 2223–2229. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

