Mot1p is essential for TBP recruitment to selected promoters during in vivo gene activation
- PMID: 12356733
- PMCID: PMC129025
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdf485
Mot1p is essential for TBP recruitment to selected promoters during in vivo gene activation
Abstract
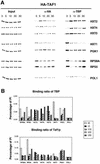
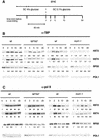
Recruitment of TATA-binding protein (TBP) is central to activation of transcription by RNA polymerase II (pol II). This depends upon co-activator proteins including TBP-associated factors (TAFs). Yeast Mot1p was identified as a general transcriptional repressor in genetic screens and is also found associated with TBP. To obtain insight into Mot1p function in vivo, we determined the mRNA expression profile of the mot1-1 temperature-sensitive (Ts) strain. Unexpectedly, this indicated that Mot1p mostly plays a positive role for transcription. For one potential activation target, HXT2, we analyzed promoter recruitment of Mot1p, TBP, Taf1p (Taf130p) and pol II by chromatin immunoprecipitation assays. Whereas TBP becomes stably associated upon activation of the HXT2 and HXT4 promoters, Mot1p showed only a transient association. TBP recruitment was compromised in two different mot1 mutant strains, but was only moderately affected in a taf1 Ts strain. Together, our data indicate that Mot1p can assist in recruitment of TBP on promoters during gene activation in vivo.
Figures




References
-
- Adamkewicz J.I., Hansen,K.E., Prud’homme,W.A., Davis,J.L. and Thorner,J. (2001) High affinity interaction of yeast transcriptional regulator, Mot1, with TATA-box binding protein (TBP). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 11883–11894. - PubMed
-
- Auble D.T., Hansen,K.E., Mueller,C.G.F., Lane,W.S., Thorner,J. and Hahn,S. (1994) Mot1, a global repressor of RNA polymerase II transcription, inhibits TBP binding to DNA by an ATP-dependent mechanism. Genes Dev., 8, 1920–1934. - PubMed
-
- Chao D.M. and Young,R.A. (1996) Activation without a vital ingredient. Nature, 383, 119–120. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

