ECM-stimulated signaling and actin reorganization in embryonic corneal epithelia are Rho dependent
- PMID: 12356822
- PMCID: PMC2745338
ECM-stimulated signaling and actin reorganization in embryonic corneal epithelia are Rho dependent
Abstract
Purpose: The goal of this study was to investigate the role of the small guanosine triphosphatase (GTPase), Rho, in the corneal epithelial response to extracellular matrix (ECM) molecules. The avian corneal epithelial model was used to establish that Rho is required for actin reorganization and tyrosine phosphorylation of integrin-mediated signal pathway proteins.
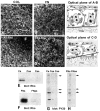
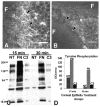
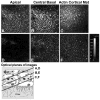
Methods: Whole embryonic corneal epithelia were isolated without the basal lamina and either transfected with Rho-specific antisense oligonucleotides or treated with Clostridium botulinum C3 exoenzyme and then stimulated with fibronectin (FN) or collagen (COL). The epithelia were evaluated for actin reorganization and protein production including Rho protein levels and tyrosine phosphorylation with Western blot analysis.
Results: After an overnight transient transfection with antisense oligonucleotides, Rho protein levels were decreased more than 80%, and tyrosine phosphorylation of all integrin-mediated signal transduction proteins was decreased compared with control epithelia. Intracellular Rho distribution did not change in the presence of antisense oligonucleotides; however, the amount of immunolabeled Rho decreased. Disrupting the signaling cascade with Rho antisense also blocked FN- and COL-stimulated actin cortical mat reformation. C. botulinum C3 exoenzyme, a pharmacologic agent that specifically causes adenosine diphosphate (ADP) ribosylation and inactivation of Rho, also blocked actin reorganization and tyrosine phosphorylation. In contrast, decreasing Raf protein levels did not change FN-mediated actin reorganization or tyrosine phosphorylation.
Conclusions: Decreasing Rho protein or blocking its function inhibited ECM-stimulated actin reorganization and signal transduction, as measured by tyrosine phosphorylation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
ROCK inhibitor (Y27632) increases apoptosis and disrupts the actin cortical mat in embryonic avian corneal epithelium.Dev Dyn. 2004 Mar;229(3):579-90. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.20008. Dev Dyn. 2004. PMID: 14991713 Free PMC article.
-
Embryonic chick corneal epithelium: a model system for exploring cell-matrix interactions.Dev Dyn. 2008 Oct;237(10):2667-75. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.21637. Dev Dyn. 2008. PMID: 18697222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ECM-stimulated actin bundle formation in embryonic corneal epithelia is tyrosine phosphorylation dependent.Anat Rec. 1999 Mar;254(3):348-59. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0185(19990301)254:3<348::AID-AR5>3.0.CO;2-5. Anat Rec. 1999. PMID: 10096666 Free PMC article.
-
Erk and PI-3 kinase are necessary for collagen binding and actin reorganization in corneal epithelia.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000 Oct;41(11):3374-82. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000. PMID: 11006227 Free PMC article.
-
[Rho-mediated signal transduction and its physiological roles].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2003 Mar;121(3):153-62. doi: 10.1254/fpj.121.153. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2003. PMID: 12673949 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Zyxin and vinculin distribution at the cell-extracellular matrix attachment complex (CMAX) in corneal epithelial tissue are actin dependent.Anat Rec. 1999 Mar;254(3):336-47. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0185(19990301)254:3<336::AID-AR4>3.0.CO;2-D. Anat Rec. 1999. PMID: 10096665 Free PMC article.
-
ROCK inhibitor (Y27632) increases apoptosis and disrupts the actin cortical mat in embryonic avian corneal epithelium.Dev Dyn. 2004 Mar;229(3):579-90. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.20008. Dev Dyn. 2004. PMID: 14991713 Free PMC article.
-
Embryonic chick corneal epithelium: a model system for exploring cell-matrix interactions.Dev Dyn. 2008 Oct;237(10):2667-75. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.21637. Dev Dyn. 2008. PMID: 18697222 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zieske JD. Perpetuation of stem cells in the eye. Eye. 1994;8:163 – 169. - PubMed
-
- Gipson I, Inatomi F. Extracellular matrix and growth factors in corneal wound healing. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 1995;6:3 – 10. - PubMed
-
- Nishida T, Tanaka T. Extracellular matrix and growth factors in corneal wounding. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 1996;7:2 – 11. - PubMed
-
- Sundarraj N, Kinchington PR, Wessel H, et al. A Rho-associated protein kinase: differentially distributed in limbal and corneal epithelia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1998;39:1266 – 1272. - PubMed
-
- Anderson SC, Sundarraj N. Regulation of a Rho-associated kinase expression during the corneal epithelial cell cycle. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2001;42:933 – 940. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

