Selective internalization of sodium channels in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons infected with herpes simplex virus-1
- PMID: 12356869
- PMCID: PMC2173241
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200204010
Selective internalization of sodium channels in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons infected with herpes simplex virus-1
Erratum in
- J Cell Biol. 2002 Nov;159(4):707.
Abstract
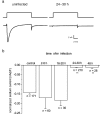
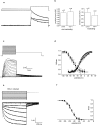
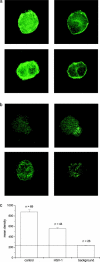
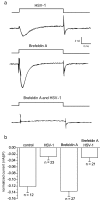
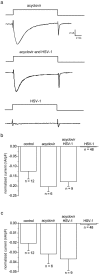
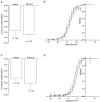
The neurotropic virus, herpes simplex type 1 (HSV-1), inhibits the excitability of peripheral mammalian neurons, but the molecular mechanism of this effect has not been identified. Here, we use voltage-clamp measurement of ionic currents and an antibody against sodium channels to show that loss of excitability results from the selective, precipitous, and complete internalization of voltage-activated sodium channel proteins from the plasma membrane of neurons dissociated from rat dorsal root ganglion. The internalization process requires viral protein synthesis but not viral encapsulation, and does not alter the density of voltage-activated calcium or potassium channels. However, internalization is blocked completely when viruses lack the neurovirulence factor, infected cell protein 34.5, or when endocytosis is inhibited with bafilomycin A(1) or chloroquine. Although it has been recognized for many years that viruses cause cell pathology by interfering with signal transduction pathways, this is the first example of viral pathology resulting from selective internalization of an integral membrane protein. In studying the HSV-induced redistribution of sodium channels, we have uncovered a previously unknown pathway for the rapid and dynamic control of excitability in sensory neurons by internalization of sodium channels.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Changes in excitability induced by herpes simplex viruses in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons.J Neurosci. 1986 Feb;6(2):391-402. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-02-00391.1986. J Neurosci. 1986. PMID: 3005524 Free PMC article.
-
The Basic Domain of Herpes Simplex Virus 1 pUS9 Recruits Kinesin-1 To Facilitate Egress from Neurons.J Virol. 2015 Dec 9;90(4):2102-11. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03041-15. Print 2016 Feb 15. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26656703 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling mechanisms of down-regulation of voltage-activated Ca2+ channels by transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 stimulation with olvanil in primary sensory neurons.Neuroscience. 2006 Aug 11;141(1):407-19. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.03.023. Epub 2006 May 6. Neuroscience. 2006. PMID: 16678970
-
Infection and Transport of Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 in Neurons: Role of the Cytoskeleton.Viruses. 2018 Feb 23;10(2):92. doi: 10.3390/v10020092. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 29473915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathophysiological roles and therapeutic potential of voltage-gated ion channels (VGICs) in pain associated with herpesvirus infection.Cell Biosci. 2020 May 24;10:70. doi: 10.1186/s13578-020-00430-2. eCollection 2020. Cell Biosci. 2020. PMID: 32489585 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The trafficking of Na(V)1.8.Neurosci Lett. 2010 Dec 10;486(2):78-83. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2010.08.074. Epub 2010 Sep 15. Neurosci Lett. 2010. PMID: 20816723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemosensory properties of murine nasal and cutaneous trigeminal neurons identified by viral tracing.BMC Neurosci. 2006 Jun 8;7:46. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-7-46. BMC Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16762059 Free PMC article.
-
Anterograde transsynaptic tracing in the murine somatosensory system using Pseudorabies virus (PrV): a "live-cell"-tracing tool for analysis of identified neurons in vitro.J Neurovirol. 2007 Dec;13(6):579-85. doi: 10.1080/13550280701586419. J Neurovirol. 2007. PMID: 18097889
-
Latent herpes simplex virus infection of sensory neurons alters neuronal gene expression.J Virol. 2003 Sep;77(17):9533-41. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.17.9533-9541.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12915567 Free PMC article.
-
Highly efficient method for gene delivery into mouse dorsal root ganglia neurons.Front Mol Neurosci. 2015 Feb 2;8:2. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2015.00002. eCollection 2015. Front Mol Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25698920 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andoh, T., K. Shiraki, M. Kurokawa, and Y. Kuraishi. 1995. Paresthesia induced by cutaneous infection with herpes simplex virus in rats. Neurosci Lett. 190:101–104. - PubMed
-
- Abriel, H., E., Kamynina, J.D. Horisberger, and O. Staub. 2000. Regulation of the cardiac voltage-gated Na+ channel (H1) by the ubiquitin-protein ligase Nedd4. FEBS Lett. 446:377–380. - PubMed
-
- Bevan, S., and N. Storey. 2002. Modulation of sodium channels in primary afferent neurons. Novartis Found. Symp. 241:144–153. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

