Activation of store-operated channels by noradrenaline via protein kinase C in rabbit portal vein myocytes
- PMID: 12356885
- PMCID: PMC2290557
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.022574
Activation of store-operated channels by noradrenaline via protein kinase C in rabbit portal vein myocytes
Abstract
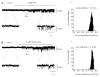
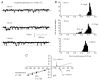
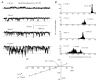
In the present study we have investigated the role of diacylglycerol (DAG) and protein kinase C (PKC) in mediating activation of Ca(2+)-permeable store-operated channels (SOCs) by noradrenaline in rabbit portal vein smooth muscle cells. With cell-attached recording, bath application of noradrenaline, 1-oleoyl-acetyl-sn-glycerol (OAG) and phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate (PDBu) evoked single channel currents. The biophysical properties of these channel currents were similar to those of the channel currents activated by depletion of internal Ca(2+) stores with cyclopiazonic acid (CPA). The activation of SOCs in cell-attached recording by noradrenaline, OAG, PDBu, CPA and the acetoxymethyl ester form of BAPTA (BAPTA-AM) was markedly inhibited by the PKC inhibitors chelerythrine and RO-31-8220. In isolated outside-out patches CPA did not evoke SOCs but noradrenaline stimulated SOC activity, which was reduced by about 90 % by PKC inhibitors. The addition of the serine/threonine phosphatase inhibitors calyculin A and microcystin also stimulated SOCs in isolated outside-out patches. It is concluded that in rabbit portal vein myocytes, noradrenaline activates SOCs via DAG and PKC, possibly by a store-independent mechanism. In addition in this cell type it appears that PKC and phosphorylation may play an important role in stimulating SOC activity in response to depletion of internal Ca(2+) stores by CPA and BAPTA-AM.
Figures




Comment in
-
SOCs - store-operated channels in vascular smooth muscle?J Physiol. 2002 Oct 1;544(Pt 1):1. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.027151. J Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12356874 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Broad LM, Braun F-J, Lieveremont J-P, Bird G, Kurosaki T, Putney JW. Role of the phospholipase-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate pathway in calcium release-activated calcium current and capacitative calium entry. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2001;276:15945–15952. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

