Anandamide is a partial agonist at native vanilloid receptors in acutely isolated mouse trigeminal sensory neurons
- PMID: 12359623
- PMCID: PMC1573524
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704904
Anandamide is a partial agonist at native vanilloid receptors in acutely isolated mouse trigeminal sensory neurons
Abstract
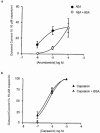
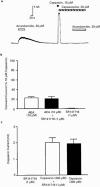
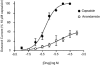
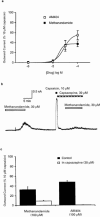
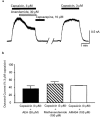
1. The endogenous fatty acid anandamide (AEA) is a partial agonist at cannabinoid CB1 receptors and has been reported to be a full agonist at the recombinant vanilloid receptor, VR1. 2. Whole cell voltage clamp techniques were used to examine the efficacy of AEA and related analogues methanandamide and N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-arachidonylamide (AM404) at native VR1 receptors in acutely isolated mouse trigeminal neurons. 3. Superfusion of the VR1 agonist capsaicin onto small trigeminal neurons voltage clamped at +40 mV produced outward currents in most cells, with a pEC(50) of 6.3+/-0.1 (maximum currents at 10-30 micro M). 4. AEA produced outward currents with a pEC(50) of 5.6+/-0.1. Maximal AEA currents (30-100 micro M) were 38+/-2% of the capsaicin maximum. AEA currents were blocked by the VR1 antagonist capsazepine (30 micro M), but unaffected by the CB1 antagonist SR141716A (1 micro M). 5. Methanandamide and AM404 were less potent than AEA at activating VR1. Methanandamide (100 micro M) produced currents 37+/-6% of the capsaicin maximum, the highest concentration of AM404 tested (100 micro M) produced currents that were 55+/-9% of the capsaicin maximum. 6. Capsazepine abolished the currents produced by AM404 (100 micro M) and strongly attenuated (>70%) those produced by methanandamide (100 micro M). 7. Co-superfusion of AEA (30 micro M, methanandamide (100 micro M) or AM404 (100 micro M) with capsaicin (3 micro M) resulted in a significant reduction of the capsaicin current. 8. These data indicate that AEA, methanandamide and AM404 activate native VR1 receptors, but that all three compounds are partial agonists when compared with capsaicin.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The actions of anandamide on rat superficial medullary dorsal horn neurons in vitro.J Physiol. 2003 Apr 1;548(Pt 1):121-9. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.035063. Epub 2003 Jan 31. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12562891 Free PMC article.
-
Anandamide and methanandamide induce both vanilloid VR1- and cannabinoid CB1 receptor-mediated changes in heart rate and blood pressure in anaesthetized rats.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2001 Dec;364(6):562-9. doi: 10.1007/s00210-001-0498-6. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11770012
-
Cannabinoid activation of recombinant and endogenous vanilloid receptors.Eur J Pharmacol. 2001 Jul 27;424(3):211-9. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(01)01153-0. Eur J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11672565
-
Possible mechanisms of cannabinoid-induced antinociception in the spinal cord.Eur J Pharmacol. 2001 Oct 19;429(1-3):93-100. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(01)01309-7. Eur J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11698030 Review.
-
Anandamide receptors.Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2002 Feb-Mar;66(2-3):377-91. doi: 10.1054/plef.2001.0349. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2002. PMID: 12052051 Review.
Cited by
-
CB1 cannabinoid receptor agonist prevents NGF-induced sensitization of TRPV1 in sensory neurons.Neurosci Lett. 2013 Sep 13;551:34-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2013.06.066. Epub 2013 Jul 12. Neurosci Lett. 2013. PMID: 23850608 Free PMC article.
-
A role for the anandamide membrane transporter in TRPV1-mediated neurosecretion from trigeminal sensory neurons.Neuropharmacology. 2005 Jul;49(1):25-39. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2005.01.031. Epub 2005 Apr 1. Neuropharmacology. 2005. PMID: 15992578 Free PMC article.
-
Citral sensing by Transient [corrected] receptor potential channels in dorsal root ganglion neurons.PLoS One. 2008 May 7;3(5):e2082. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002082. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18461159 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of the palmitoylethanolamide analogue, palmitoylallylamide (L-29) on pain behaviour in rodent models of neuropathy.Br J Pharmacol. 2007 Aug;151(7):1117-28. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707326. Epub 2007 Jun 11. Br J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17558434 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of transient receptor potential vanilloid subtype 1 and cannabinoid type 1 receptors in the brain: neuroprotection versus neurotoxicity.Mol Neurobiol. 2007 Jun;35(3):245-54. doi: 10.1007/s12035-007-0030-1. Mol Neurobiol. 2007. PMID: 17917113 Review.
References
-
- AHLUWALIA J., URBAN L., CAPOGNA M., BEVAN S., NAGY I. Cannabinoid 1 receptors are expressed in nociceptive primary sensory neurons. Neuroscience. 2000;100:685–688. - PubMed
-
- BOGER D.L., SATO H., LERNER A.E., HEDRICK M.P., FECIK R.A., MIYAUCHI H., WILKIE G.D., AUSTIN B.J., PATRICELLI M.P., CRAVATT B.F. Exceptionally potent inhibitors of fatty acid amide hydrolase: the enzyme responsible for degradation of endogenous oleamide and anandamide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2000;97:5044–5049. - PMC - PubMed
-
- BURKEY T.H., QUOCK R.M., CONSROE P., EHLERT F.J., HOSOHATA Y., ROESKE W.R., YAMAMURA H.I. Relative efficacies of cannabinoid CB1 receptor agonists in the mouse brain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1997;336:295–298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

